Search Results
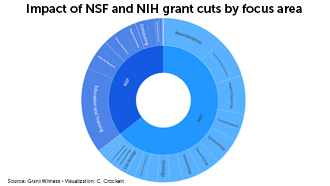
Are cutbacks cutting our future?
In 2025, the Trump administration froze or terminated more than 3,800 research grants from the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation. The roughly $3 billion in cuts targeted initiatives related to diversity, equity and inclusion; environmental protection; vaccine hesitancy; public health and more.
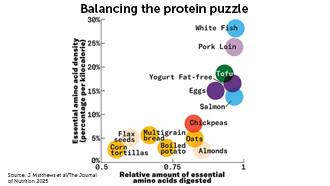
Balancing the protein puzzle
Protein is having a moment. It’s cropping up as an additive in all sorts of foods, and social media influencers tout high-protein diets as key to big muscles. But people in the United States typically get enough protein; they just might not be getting the right mix.
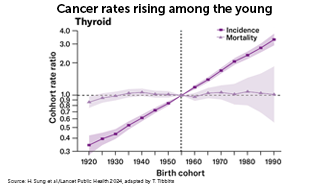
Cancer patterns in younger generations
Cancer is typically a disease of older people. But since the 1990s, rates of early onset cancer have been rapidly increasing globally.

Eyes are not all equal
Golden apple snails can completely regrow a functional eye within months of having lost one. Understanding how the snails re-create or repair their eyes might someday lead to therapies to heal people’s eye injuries or reverse some eye diseases.

Mapping the Mississippi
Freshwater fish make vast treks, but their migrations remain hidden beneath the surfaces of rivers. This invisibility has left freshwater fish largely overlooked, even as their populations worldwide have plummeted. Now, global “swimways” for migratory fish are emerging as an important conservation focus.
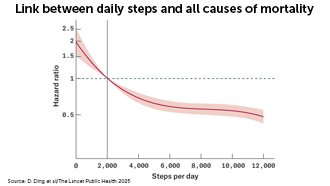
Take a hike
Walking just 7,000 steps per day can lower a person’s risk of certain health issues, according to a new study. Even a small increase in steps per day lowered health risks.
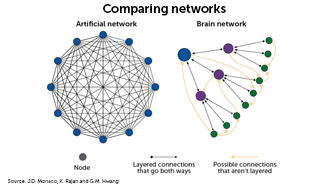
Wiring the mind
Researchers are drawing inspiration from the brains of creatures from worms to humans to develop more efficient, more capable forms of AI.
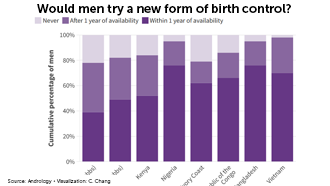
The rise of male contraceptive options
Contraceptive pills for women emerged in 1960, followed by hormonal implants, patches, vaginal rings and IUDs. But no new contraceptive methods have become available for men. New research could change that in the next five to 10 years.
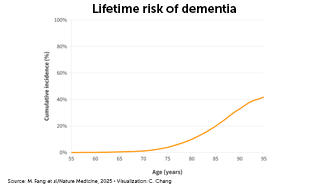
U.S. dementia cases on the rise
Scientists predict that, by 2060, one million U.S. adults per year will develop dementia. The new estimate surpasses previous estimates of how many people will struggle with memory, reasoning and language difficulties that interfere with life.
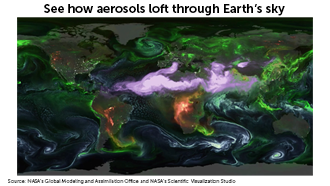
Aerosols in the air: Art in motion?
The atmosphere abounds with aerosols, tiny particles with large sway over global temperature. A new visualization from NASA reveals how these airborne particles swirl through Earth’s sky.
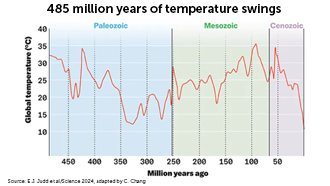
Earth’s history of temperature shifts
Earth’s climate doesn’t have to look like it does now. In fact, it usually hasn’t. Across 4.5 billion years, geologic forces have shaped the planet’s climate from its fiery infancy to the (for now) chilly present. Studying these changes may help us understand what may happen next because of climate change.
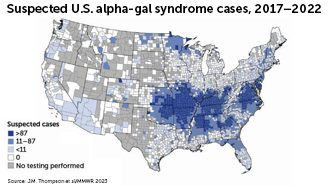
Mapping the spread of ticks
Three types of ticks may spread alpha-gal syndrome, an allergy to red meat. Researchers think the condition is caused by molecules in the saliva of certain tick species. The best way to avoid the syndrome is to prevent tick bites.