Search Results
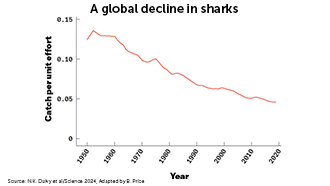
Save our Sharks!
Many people fear sharks even though it’s more likely for someone to be struck by lightning than bitten by a shark. People should instead fear for sharks, many of which are threatened. Researchers are working to convince people that sharks, which are vital to maintaining the ocean’s health, are more valuable alive than dead.
Ecosystem portrait
In this activity, students will read the Science News Explores article “There’s life beneath the snow — but it’s at risk of melting away” and reflect on how the author of the article educates the reader. After finishing the article, students will create their own ecosystem portrait to educate their classmates about a unique ecosystem.
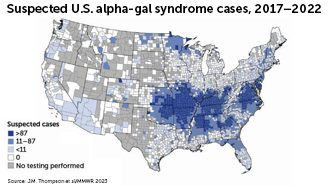
Mapping the spread of ticks
Three types of ticks may spread alpha-gal syndrome, an allergy to red meat. Researchers think the condition is caused by molecules in the saliva of certain tick species. The best way to avoid the syndrome is to prevent tick bites.
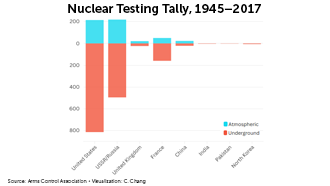
Nuclear testing tally
Beginning with the first test explosion in 1945, more than 2,000 atomic blasts have rattled the globe. Nuclear testing dwindled after a treaty in the 1990s. Recently, some in the United States have called for resumed testing, which could have serious consequences for the environment and global politics.
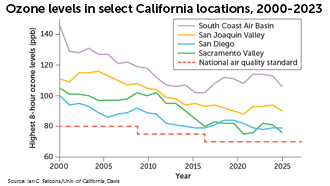
Agriculture may be growing ozone
The air pollutant ozone has been linked to health problems including respiratory illness, reproductive problems and some cancers. Levels of ozone in the United States have come down over time but have started to rise again in places because of wildfires and soil emissions.
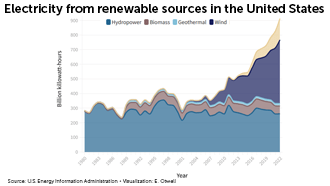
Renewable power is a bright idea
Over the past two decades, electricity from renewable sources, such as wind and solar, has been on the rise. Devices known as grid-forming inverters will likely play a major role in getting renewable energy safely into the power grid.
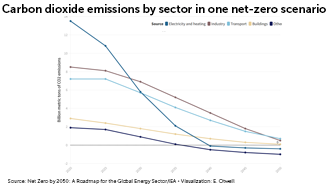
The race to net zero
Drastic cuts to greenhouse emissions are needed to prevent even more catastrophic consequences than the rising sea levels, extreme weather and other impacts our warming world has already faced. Scientists have mapped out potential paths to net-zero, when greenhouse gases emitted are balanced by those removed. This includes decreases in emissions from transportation, industry and other sectors.
Fungal Solutions
Across the planet, people throw away over
two billion metric tons of waste every year. That waste feeds into environmental problems from climate change to pollution. So how can we reduce the amount of waste we produce? In this activity, students will categorize and record the waste they produce daily and reflect on the amount of “invisible” waste produced before they receive products. Students will then identify solutions for reducing each category of waste.
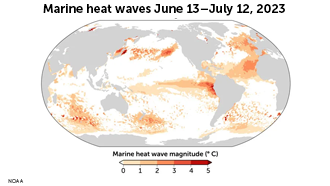
Analysis of marine heat waves
Global temperatures are at an all-time high due to the compounded effects of climate change and El Nino. Oceans around the world are warming at an alarming rate. In summer 2023, some 40 percent of the world’s oceans were affected by heat waves.
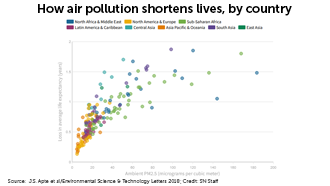
Air pollution and human health
In August of 2018, scientists published research showing how air pollution shaves off about a year on average from human life expectancy. In more polluted regions of Asia and Africa, lives are shortened by 1.5–2 years on average. Loss in life expectancy rises with increasing concentrations of fine particulate air pollution (PM2.5).
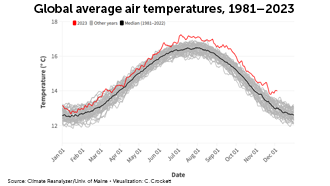
Hottest year on record
Since temperature record-keeping began 150 years ago, the 12-month period from November 2022 through October 2023 was the hottest on record until temperatures in 2024 exceeded those in 2023. The heat raised sea surface temperatures, melted sea ice and endangered human health.
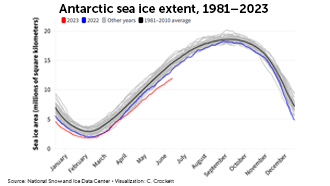
Antarctic sea ice
In 2023, the expanse of floating ice encircling Antarctica hit record lows throughout the year. Scientists expect dramatic declines in sea ice at Earth’s other pole but hadn’t observed major changes in the Antarctic until the last few years.