Search Results
The art of chemical predation
Predation occurs when one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. In this lesson, students will learn about the recently discovered chemical predation tactics of the feather-legged lace weaver spider, which vomits toxins on its prey. Students will explore the possible evolutionary advantages and disadvantages of this technique and research another organism that uses chemical means for predation.
Tracking dinos
T. rex or Velociraptor — who would win in a race? Scientists of the 1970s developed a set of equations that led modern scientists to predict speed of dinosaurs. But how well do those equations predict real life? Learn how a tidy math equation can sometimes oversimplify complex issues. Answer questions about how missing variables might lead to flawed conclusions and discuss challenges from inferring the behavior and characteristics of long-extinct species from available evidence.
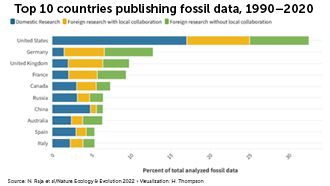
Parachute paleontology
Fossil research has been plagued by parachute paleontology. This happens when scientists from high-income countries travel to low-income countries to study or collect fossils but don’t involve local experts. Sometimes foreign scientists skirt local laws about exporting fossils or buy them under sketchy or even illegal circumstances.
Present day dinos
By studying fossils, scientists have nailed down the evolutionary connection between birds and dinosaurs. Students will consider how changes to the way some species are now classified highlight the evolutionary relationship between birds and dinosaurs. This guide also will discuss evidence for this relationship using an example fossil.
Springtail research design and data analysis
Scientists have discovered that Dicyrtomina minuta, a species of globular springtail, can perform the fastest backflip of any animal on Earth. Use this discussion to have students review how the research team studied springtail backflips by analyzing high-speed footage.
Then, in this related activity by DataClassroom, have students analyze graphs of the springtail research data to learn about the linear velocity, angular velocity, linear acceleration and rotational acceleration of springtail flips using this Stacked Graphs and Biophysics with Spring-Loaded Arthropods activity. Create a free account to view the student-facing dataset and activity within the DataClassroom web application. View the teacher answer key here.
Then, in this related activity by DataClassroom, have students analyze graphs of the springtail research data to learn about the linear velocity, angular velocity, linear acceleration and rotational acceleration of springtail flips using this Stacked Graphs and Biophysics with Spring-Loaded Arthropods activity. Create a free account to view the student-facing dataset and activity within the DataClassroom web application. View the teacher answer key here.
Assembly of Amazing Adaptations
To survive, creatures need to be able to sense many aspects of their environment, including food options. Scientists have recently discovered that the northern sea robin, an oceanic fish, has legs used for walking and also for tasting, to find buried meals. Begin a unit on natural selection/evolution by reviewing what these terms mean. Then, provide example organisms to explore their different types of adaptations (structural, physiological and behavioral). Finally, have students create their own species with adaptations specific to unique human- or natural disaster-influenced habitats.
Photoluminescent Bat Toes
Biologists didn't design their experiments looking for glow-in-the-dark feet, but sometimes scientific failures yield surprising discoveries. If glowing toes sound batty to you, learn how scientists illuminate the secrets of a flighty mammal while answering questions about the scientific process.
Arthropod Olympics
A recent study found that a species of globular springtail can perform the fastest backflip of any animal on Earth. In this activity, students will research another Olympics-worthy arthropod competitor and describe how they’d measure performance in their imagined sports event.
Pairing up to create proteins
Scientists studied ancient woolly mammoth DNA that had been freeze-dried in place, preserving it and retaining its shape. The researchers adapted a technique for studying the structures of chromosomes within a nucleus to determine which genes were turned on and off in the mammoth genome. In this activity, students will review what happens when genes are turned on by completing exercises that illustrate hypothetical DNA base pairing and simplified examples of transcription and translation.
Turning genes on and off
Scientists have been able to study genetic activity in an ancient woolly mammoth’s DNA, thanks to a new method. Learn about the research study and the preservation of the DNA while thinking through the implications of having certain genes turned on or off.
Organism Observations
Students will observe animal behavior via live camera feed and reflect on their observations. Then they will learn about how animal behaviorists use camera traps and field observations to infer meaning from animal behaviors.
Data on dwindling migratory species
Students will analyze and compare two graphs to summarize a recent report about animals protected by an international treaty called the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals before discussing the possible next steps and limitations of the treaty.