Search Results
Friends and foes: Exploring symbiosis and predation in nature
Have students explore ecological relationships among organisms through a case study on a newly identified fungus named after biologist Sir David Attenborough that zombifies spiders — taking over their bodies before killing them. Students will compare and contrast commensalism, mutualism, parasitism and predation and then use the definitions to identify examples.
The case of the haunted railroad
Strange ghostly blue lights have haunted the little town of Summerville, S.C. for decades. Reports of spectral balls of light floating along a desolate stretch of railroad inspired a ghostly local legend. Learn how legends can inspire real-world science. Then discuss similarities and differences between scientific theory and legend while answering questions about a proposed geologic explanation for this phenomenon.
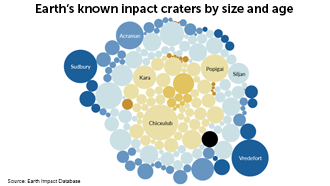
Earth’s impact craters
Space rocks that have smashed into our planet have left impact craters. Many of the craters have been wiped away by erosion, but scientists have cataloged the survivors, including some that are over one billion years old.
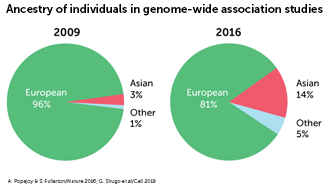
Genetic genome gaps cause blind spots
Scientists have had a rough draft of the human genome for some 20 years. They hoped to use it for precision medicine, treatments based on an individual’s DNA. But an understanding of the differences between different people’s DNA has been hampered by a lack of diversity in genetic studies known as genome-wide association studies.

All About STEM Comics, 3-2-1 Strategy and An Atmospheric Electric Field
Use these lesson plans paired to articles from the April issue of Science News Explores to introduce students to STEM comic strips that tell the stories of animal research studies and have them create their own, download a 3-2-1 literacy template to use with any article and cover concepts of electrical fields in Earth’s atmosphere.
All about STEM Comics, called Wild Things: An article type from Science News Explores
How can comic strips help teach experimental design of research studies? Use this lesson plan to learn about an article type called Wild Things that is published by Science News Explores in print and online. Wild Things use comic strips that tell the stories of research studies on animals’ biology and behavior. You can also access a lesson plan template that can be used with any Wild Things article.
Where force fields collide
Scientists have long suspected that a mysterious third force underlies the unique life-sustaining conditions of our planet but lacked the technology to measure it. Until now, that is. Learn how the interplay between different planet-wide energy forces gives rise to Earth’s cozy atmosphere. Then, explore how scientists use modern technology to study a newly discovered electrical field and fit this knowledge into their global understanding of how our planet supports life.
Literacy Practice: 3-2-1 Strategy
Use this lesson plan and the provided template to have your students practice the 3-2-1 strategy. This literacy strategy is a quick way to check students’ understanding of a concept, reading or lesson. It helps them summarize and organize their thoughts by listing three responses to one prompt, two responses to another prompt and one response to a final prompt.

A Crumbling Exoplanet and Marsupial Moles
Incorporate articles from the March issue of Science News to learn how scientists are using data from the James Webb Space Telescope to find out what exoplanets might be made of and investigate common characteristics among organisms using phylogenetic trees and cladograms.
Exoplanet spills its guts
Scientists just caught a rare glimpse of an exoplanet’s innards. Learn how scientists use wavelength data from the James Webb Space Telescope to figure out what exoplanets might be made of. Answer questions about the value of personification as a literary device, all the while discussing how knowledge gleaned from one discovery can help scientists answer new and lingering questions.
Uncovering the ancestry of the marsupial mole
Use scientists’ latest findings about marsupial moles to have students explore natural selection. Students will use figures that depict evolutionary relationships among organisms — phylogenetic trees and cladograms — to trace ancestry and common characteristics. Then they will apply this knowledge by investigating common characteristics of different taxonomic groups associated with the marsupial mole, illustrating why this animal has been particularly hard to categorize and study.
Fungal Solutions
Across the planet, people throw away over
two billion metric tons of waste every year. That waste feeds into environmental problems from climate change to pollution. So how can we reduce the amount of waste we produce? In this activity, students will categorize and record the waste they produce daily and reflect on the amount of “invisible” waste produced before they receive products. Students will then identify solutions for reducing each category of waste.