
McKenzie Prillaman
Staff Writer
McKenzie Prillaman is a science and health journalist based in Washington, DC, who interned at Science News in spring 2023. She holds a degree in neuroscience from the University of Virginia and studied adolescent nicotine dependence at the National Institute on Drug Abuse. After figuring out she’d rather explain scientific research than conduct it, she worked at the American Association for the Advancement of Science and then earned a master’s degree in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz. Her work has appeared in Nature, Scientific American, The Cancer Letter and The Mercury News, among other publications.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by McKenzie Prillaman
-
 Oceans
OceansHow will the LA fires affect the ocean? These researchers are racing to find out
Scientists aboard a research vessel near Los Angeles collected ash, air and water samples as fire blazed on the hills before them in January.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThis caterpillar wears the body parts of insect prey
Dubbed the “bone collector,” this caterpillar found on a Hawaiian island disguises itself while stalking spider webs for trapped insects to eat.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineClinical trials face uncertain futures amid Trump cuts
The Trump administration has reportedly disrupted over 100 clinical trials. Science News spoke to researchers about the impacts on four of them.
-
 Space
SpaceFermenting miso in orbit reveals how space can affect a food’s taste
A miso test on the International Space Station shows fermenting food is not only possible in space, it adds nuttier notes to the Japanese condiment.
-
 Plants
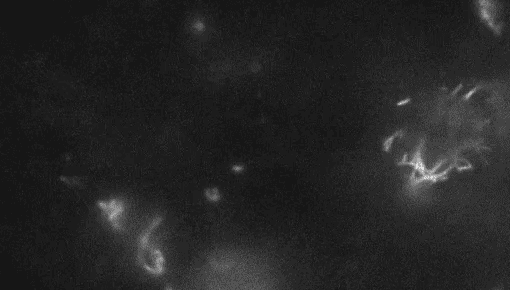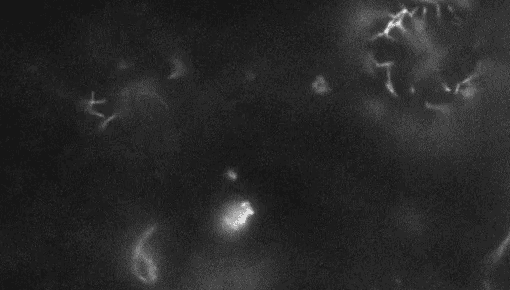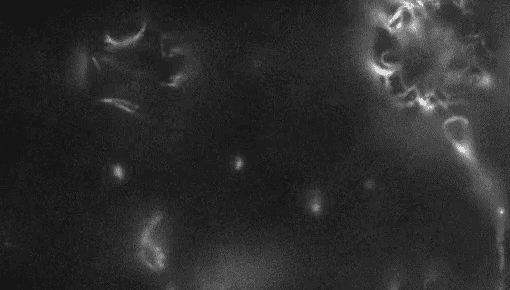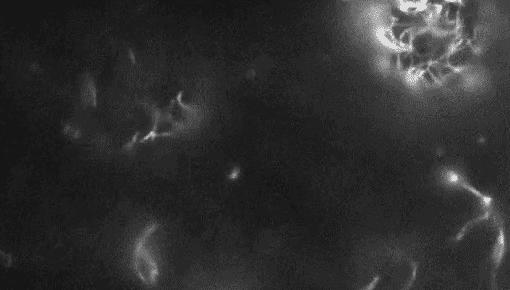
PlantsWatch live plant cells build their cell walls
Imaging wall-less plant cells every six minutes for 24 hours revealed how the cells build their protective barriers.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGray seals may sense their own blood oxygen levels
The seals’ ability to detect the amount of oxygen in their blood may help them make diving decisions and avoid drowning.
-
 Space
SpaceTwo astronauts stuck in space for 9 months have returned to Earth
Astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore’s extended stay in the International Space Station will add to what we know about how space affects health.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeasles is spreading. Here’s what experts say you should know
The uptick in measles cases has left many people wondering about early signs of measles, whether they need an updated vaccine and treatment options.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNarwhals may use their iconic tusks to play
Videos show narwhals using their tusks in several ways, including prodding and flipping a fish. It’s the first reported evidence of the whales playing.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceParenthood may help the brain stay young
A study of nearly 38,000 adults shows that the number of kids correlates with coordination of brain regions’ activities — regardless of parents’ sex.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society5 years after COVID-19 became a pandemic, are we ready for what’s next?
We’ve learned a lot about COVID-19 over the last five years, but big questions remain. Recent federal actions may hinder the disease’s management.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese scientists have a plan to demystify the vaginal microbiome
Vaginal microbes play a huge role in overall health, but researchers know relatively little about them. Citizen science could help change that.