
Animals
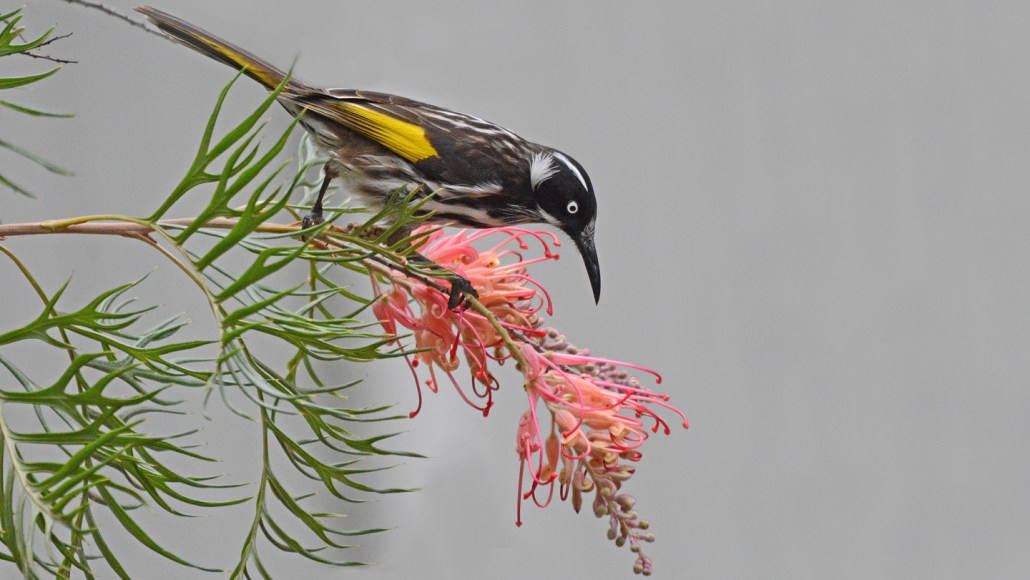
Here’s how honeyeaters and other birds thrive on sugary diets
Birds that feed on nectar or fruit evolved better mechanisms for managing metabolism, blood pressure and high glucose.
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Birds that feed on nectar or fruit evolved better mechanisms for managing metabolism, blood pressure and high glucose.
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.

Finding a caterpillar with rhythm was “mind-blowing,” suggesting it might be a more widespread part of animal communication than thought.

Fecal analyses and necropsies suggest a fire-footed rope squirrel was the source of a 2023 mpox outbreak among sooty mangabeys in Côte d’Ivoire.
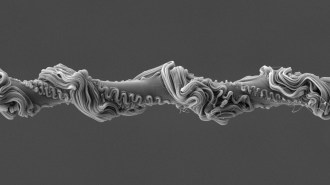
Rufous net-casting spiders can tune the stiffness and elasticity of their webs thanks to loops of silk, scanning electron microscope images reveal.

During a test drive, the mobile lab van uncovered a drug-resistant HIV strain that sprung up after the ongoing war with Russia started.

A new study suggests that inherited traits explain a small but measurable share of why some people relocate far from where they were born.

The TRPV4 protein’s dual nature, found in studies with mice, may complicate the hunt for human itch treatments

A flexible tongue, sensitive beak and teethlike cones in the mouth may have helped Archaeopteryx generate enough energy to fly.

Research reveals more short-snouted dogs besides pugs and bulldogs that struggle with breathing. Pekingese and Japanese Chins topped the study's list.

The findings strengthen the case that regeneration is an old trait, offering insights into how complex tissues rebuild themselves.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber?
Become one now.