Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhy is math harder for some kids? Brain scans offer clues
Kids with math learning disabilities process number symbols differently than quantities shown as dots — and it shows up in MRIs.
By Lily Burton -
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s how honeyeaters and other birds thrive on sugary diets
Birds that feed on nectar or fruit evolved better mechanisms for managing metabolism, blood pressure and high glucose.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMosquitoes began biting humans more than a million years ago
A DNA analysis suggests mosquitoes shifted from nonhuman primates to early humans nearly 2 million years ago.
By Tom Metcalfe - Animals
Climate change could threaten monarch mass migration
Suitable milkweed habitat in Mexico may shift south, fracturing existing migration routes and possibly pushing some butterflies to stay put.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKeeping a beat wins caterpillars friends in low places
Finding a caterpillar with rhythm was “mind-blowing,” suggesting it might be a more widespread part of animal communication than thought.
By Jake Buehler -
 Life
LifeAn African monkey ate a rope squirrel and came down with mpox
Fecal analyses and necropsies suggest a fire-footed rope squirrel was the source of a 2023 mpox outbreak among sooty mangabeys in Côte d’Ivoire.
-
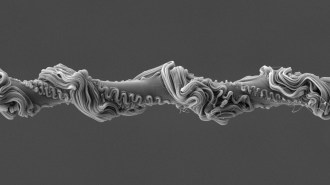 Animals
AnimalsIntricate silk helps net-casting spiders ensnare prey in webs
Rufous net-casting spiders can tune the stiffness and elasticity of their webs thanks to loops of silk, scanning electron microscope images reveal.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA lab on wheels is tracking HIV spread in war-torn Ukraine
During a test drive, the mobile lab van uncovered a drug-resistant HIV strain that sprung up after the ongoing war with Russia started.
By Kamal Nahas -
 Genetics
GeneticsWanderlust may be written in our DNA
A new study suggests that inherited traits explain a small but measurable share of why some people relocate far from where they were born.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis itch-triggering protein also sends signals to stop scratching
The TRPV4 protein’s dual nature, found in studies with mice, may complicate the hunt for human itch treatments
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyA mouth built for efficiency may have helped the earliest bird fly
A flexible tongue, sensitive beak and teethlike cones in the mouth may have helped Archaeopteryx generate enough energy to fly.
By Jay Bennett -
 Animals
AnimalsSome dog breeds carry a higher risk of breathing problems
Research reveals more short-snouted dogs besides pugs and bulldogs that struggle with breathing. Pekingese and Japanese Chins topped the study's list.
By Jake Buehler