
Meghan Rosen is a senior writer who reports on the life sciences for Science News. She earned a Ph.D. in biochemistry and molecular biology with an emphasis in biotechnology from the University of California, Davis. Her dissertation work involved studying mutated proteins in liver and kidney cancer. She later graduated from the science communication program at UC Santa Cruz. Prior to joining Science News in 2022, she was a media relations manager at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. Her work has appeared in Wired, Science, and The Washington Post, among other outlets. Once for McSweeney’s, she wrote about her kids’ habit of handing her trash, a story that still makes her (and them) laugh.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Meghan Rosen
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow does early pregnancy lower breast cancer risk? Odd cells could offer clues
Suspicious cells build up in mice that haven’t given birth, a new study finds. They could help explain a longstanding mystery of breast cancer biology.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOver 40? Your rotator cuff probably looks a little rough
MRI scans of over 600 Finnish adults found that nearly all had frayed, torn or otherwise abnormal rotator cuffs — yet most had no symptoms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMeds like Ozempic could ease arthritis
A study in mice and people with osteoarthritis suggests semaglutide can bulk up cartilage between bones, though bigger trials are needed to confirm.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGum disease bacteria can promote cancer growth in mice
In mice, the oral bacteria F. nucleatum can travel to mammary tissue via the bloodstream, where it can damage healthy cells.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow Greenland sharks defy aging
When it comes to bucking the biological ails of aging, humans could learn something from Greenland sharks.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThese medical breakthroughs and advances gave patients new hope in 2025
Advances delivered what may feel like medical miracles, including the first bladder transplant, a lifesaving personalized gene therapy and more.
-
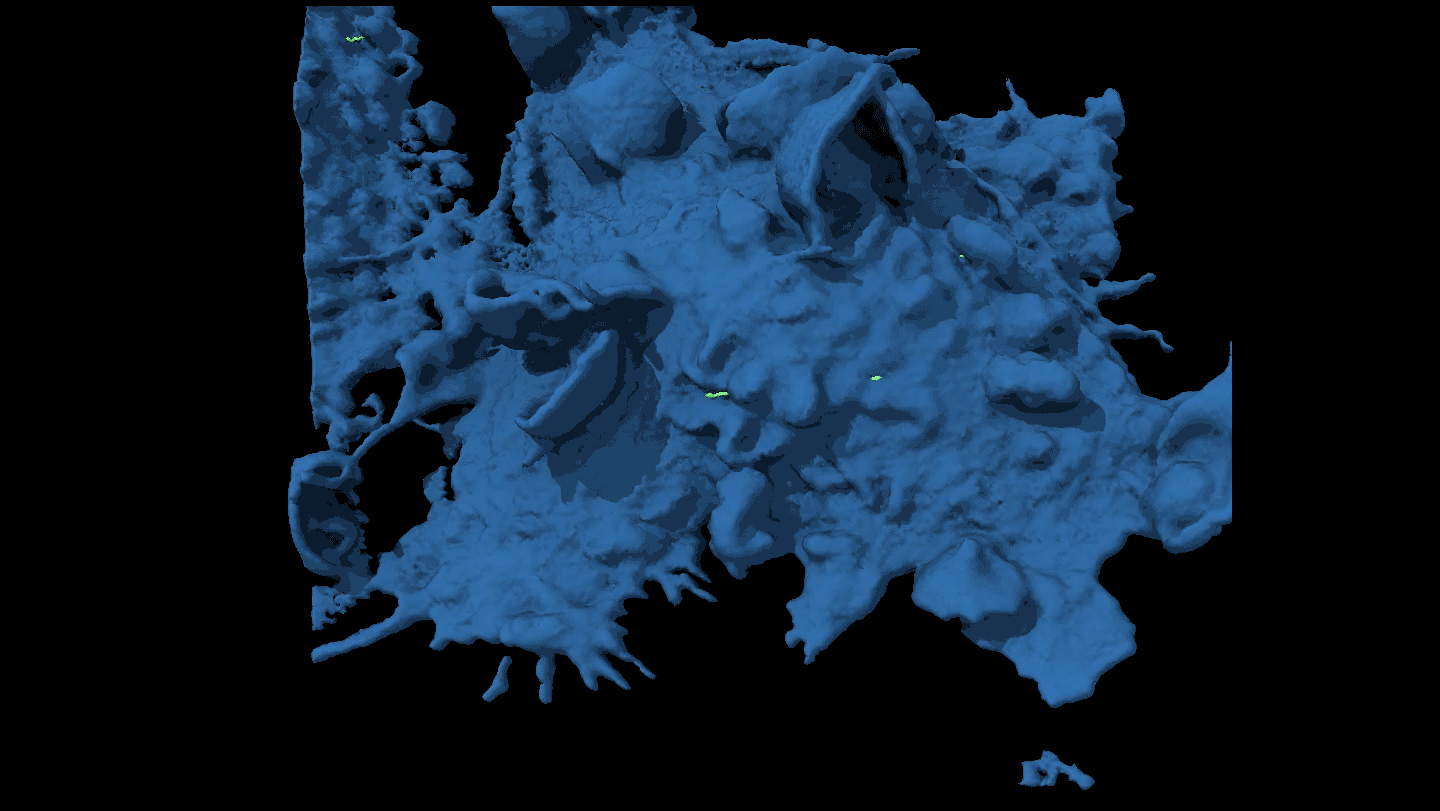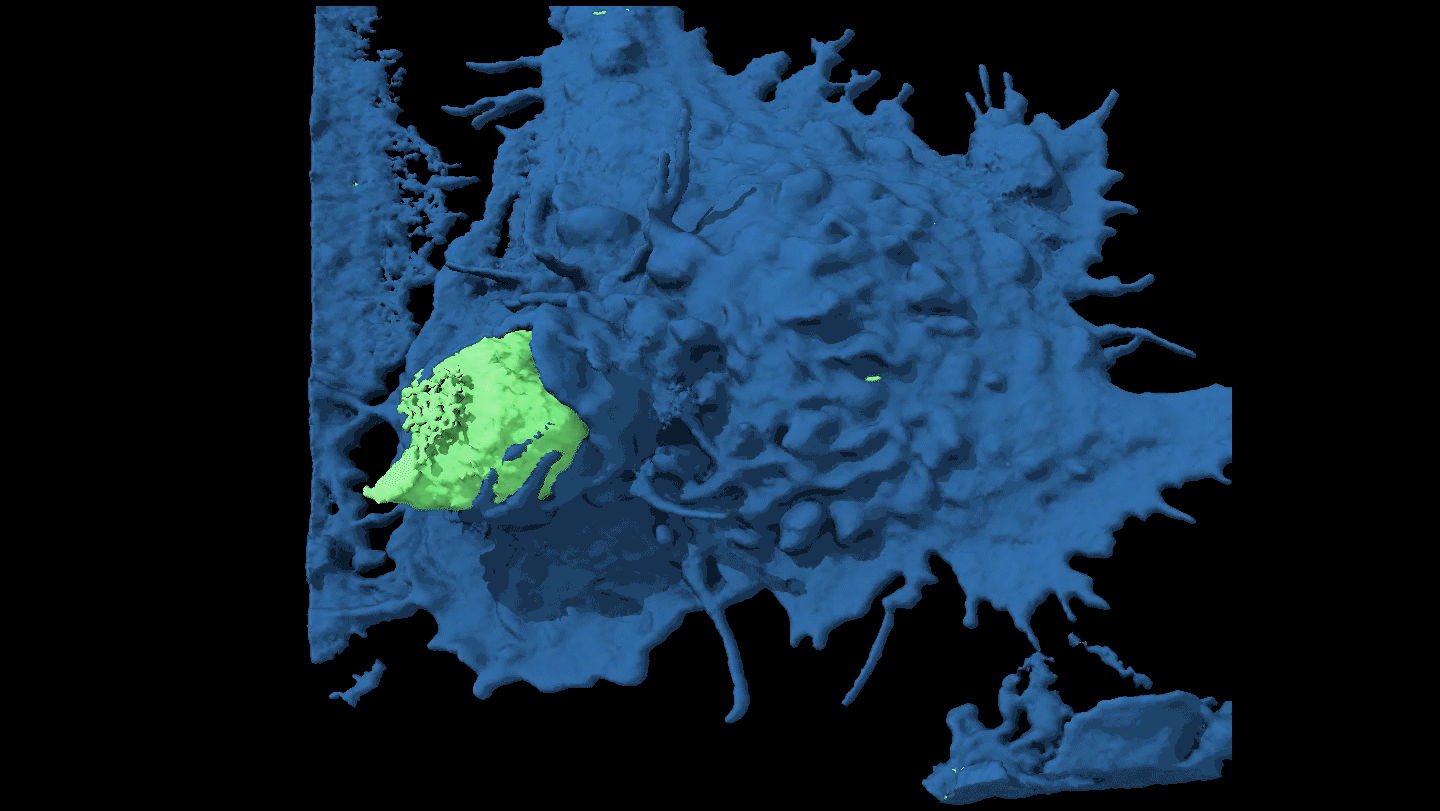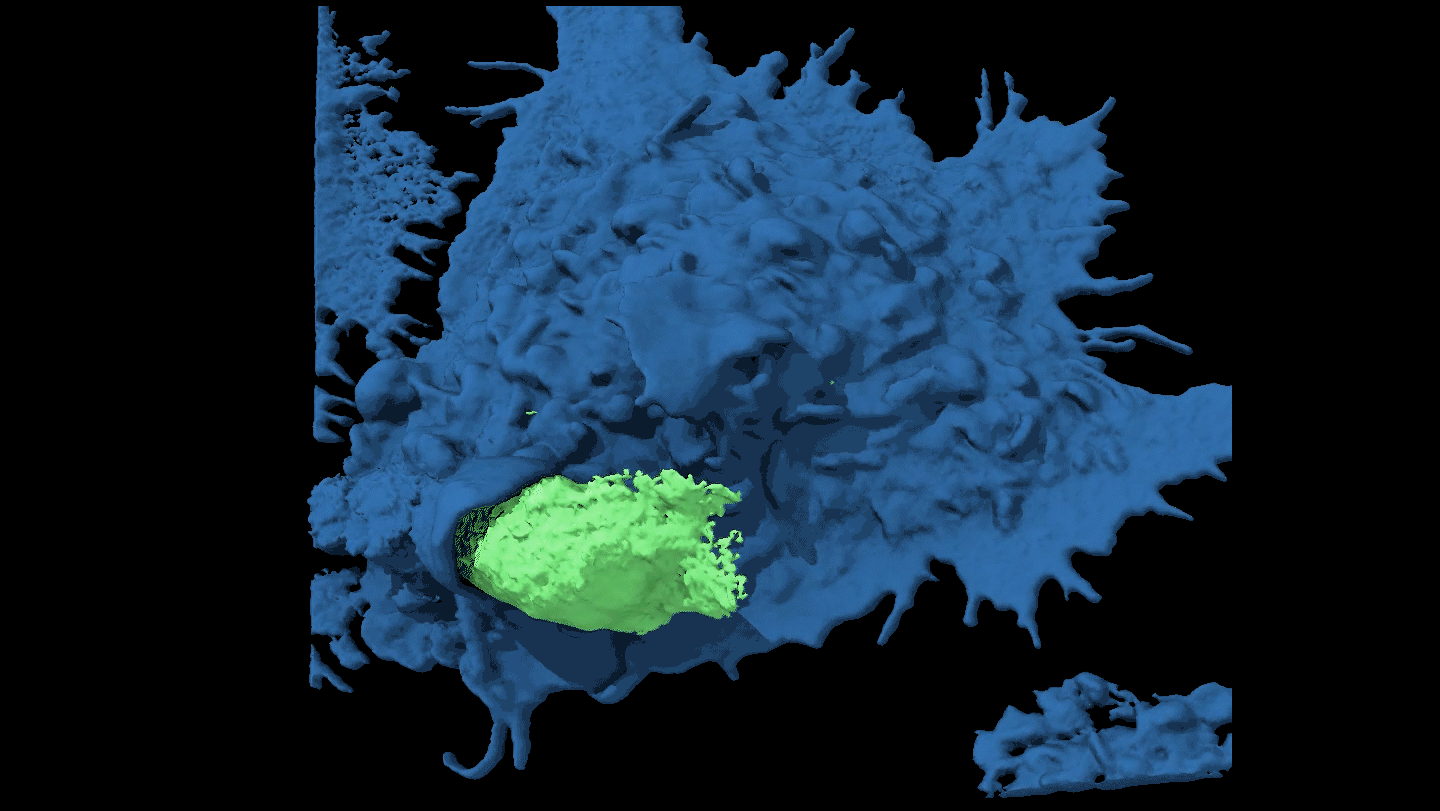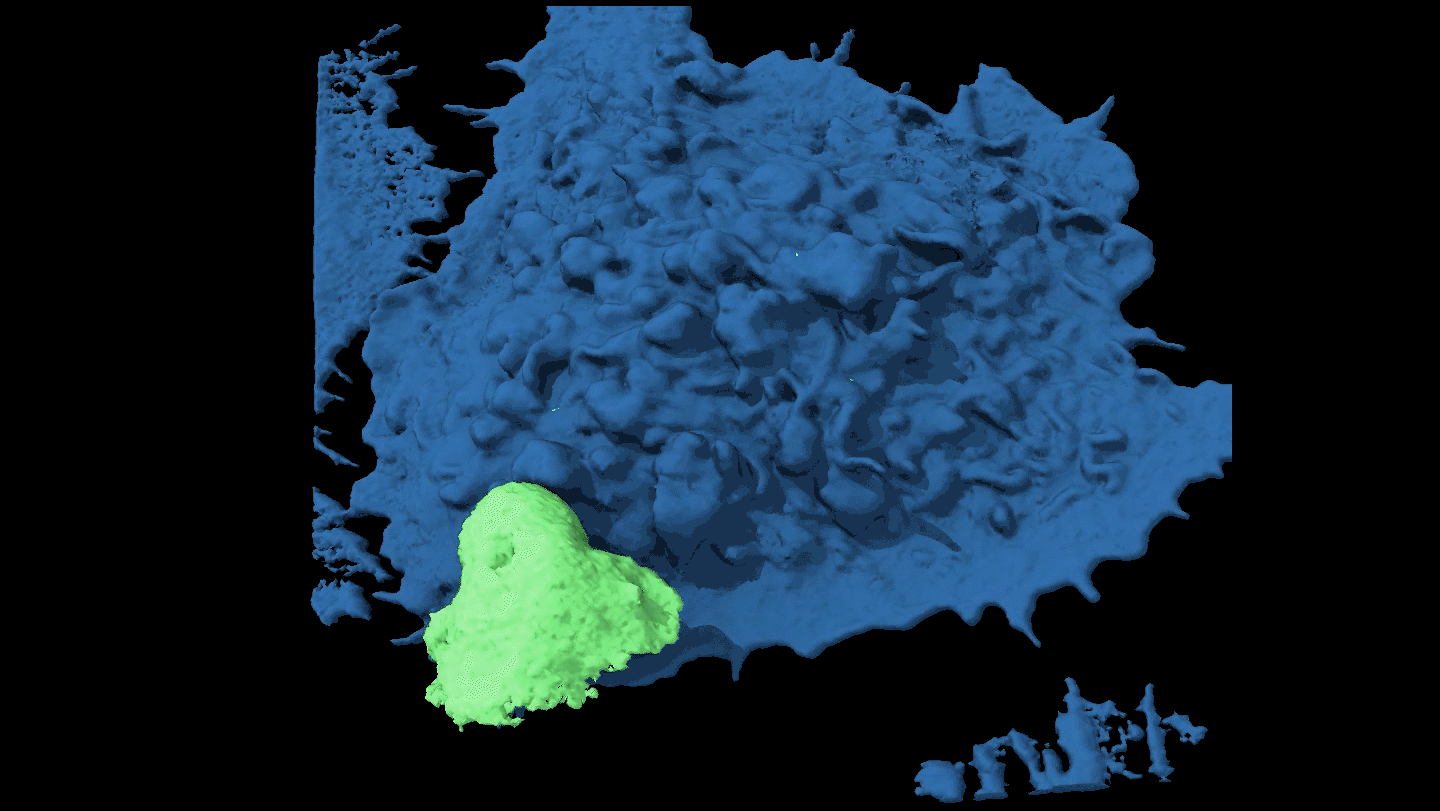 Life
LifeWatch a cancer cell evade capture
By moving around, some cancer cells force attacking immune cells to just nibble at the edges rather than engulf them completely.
-
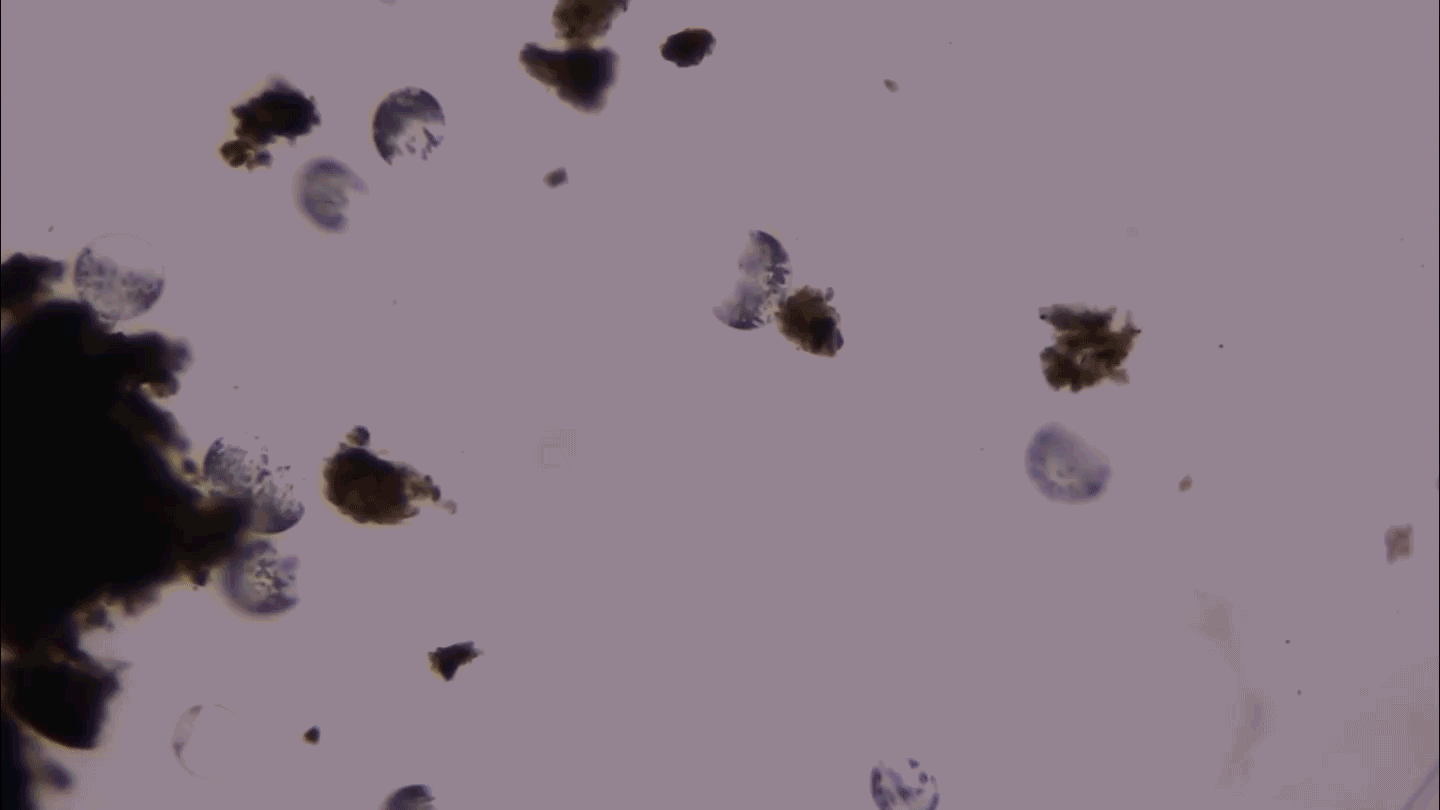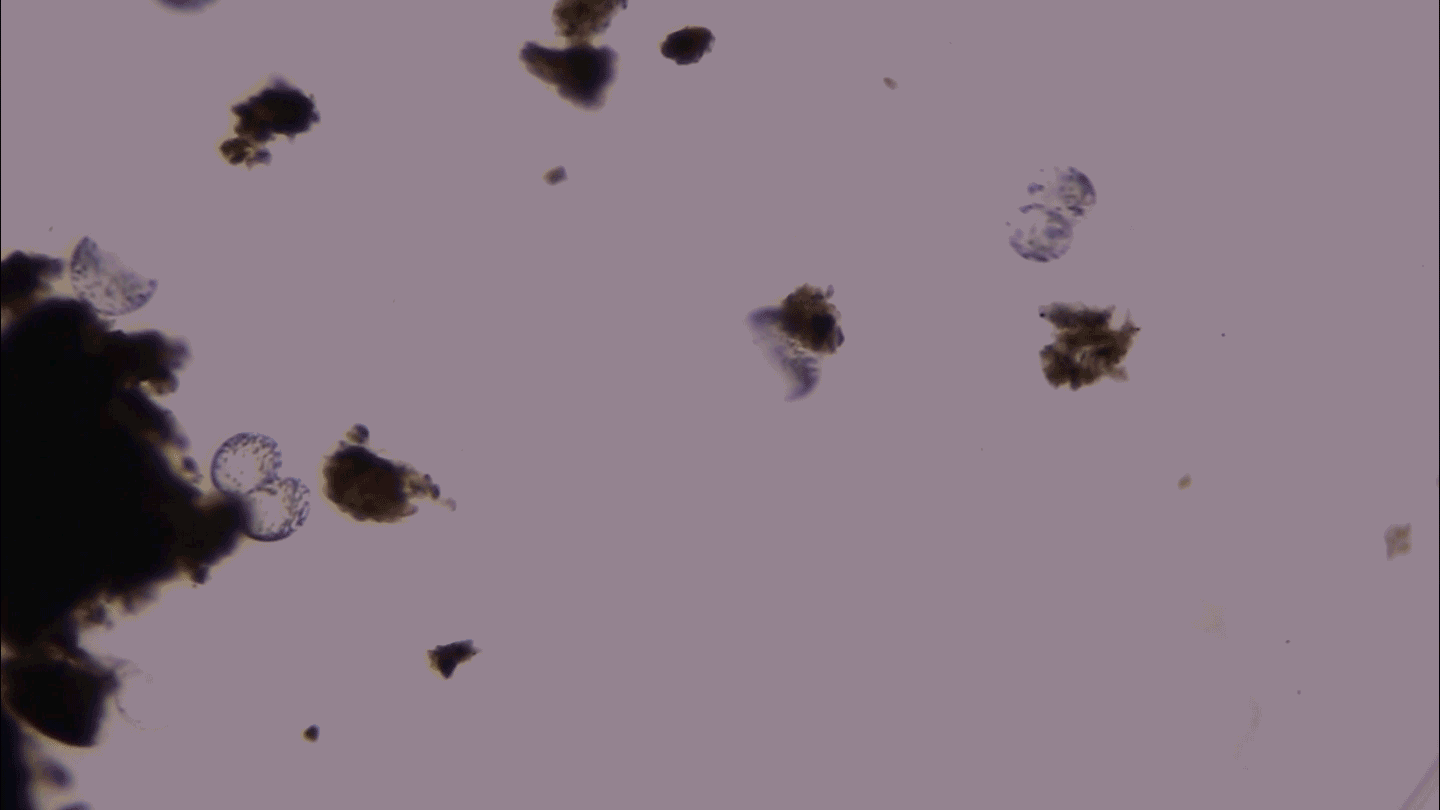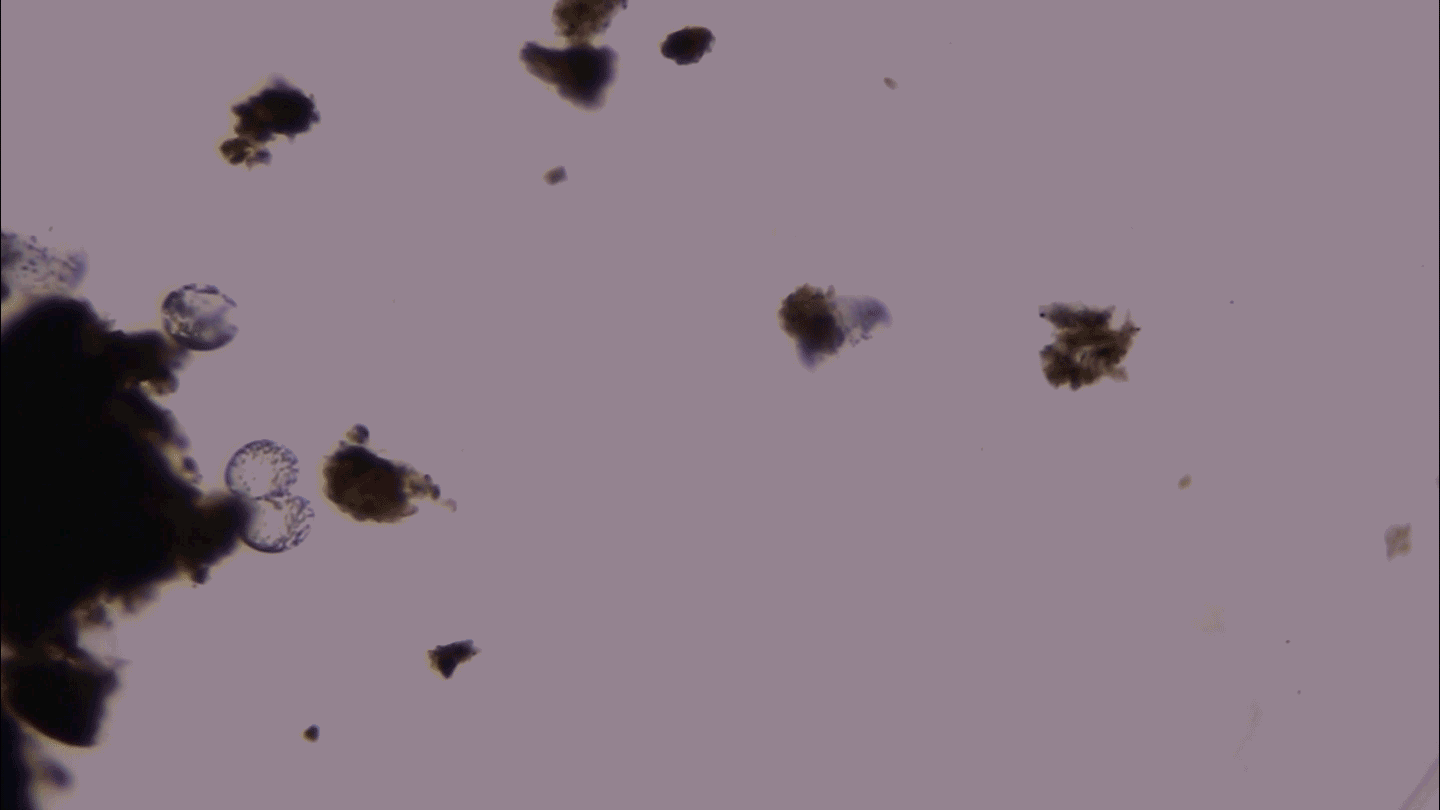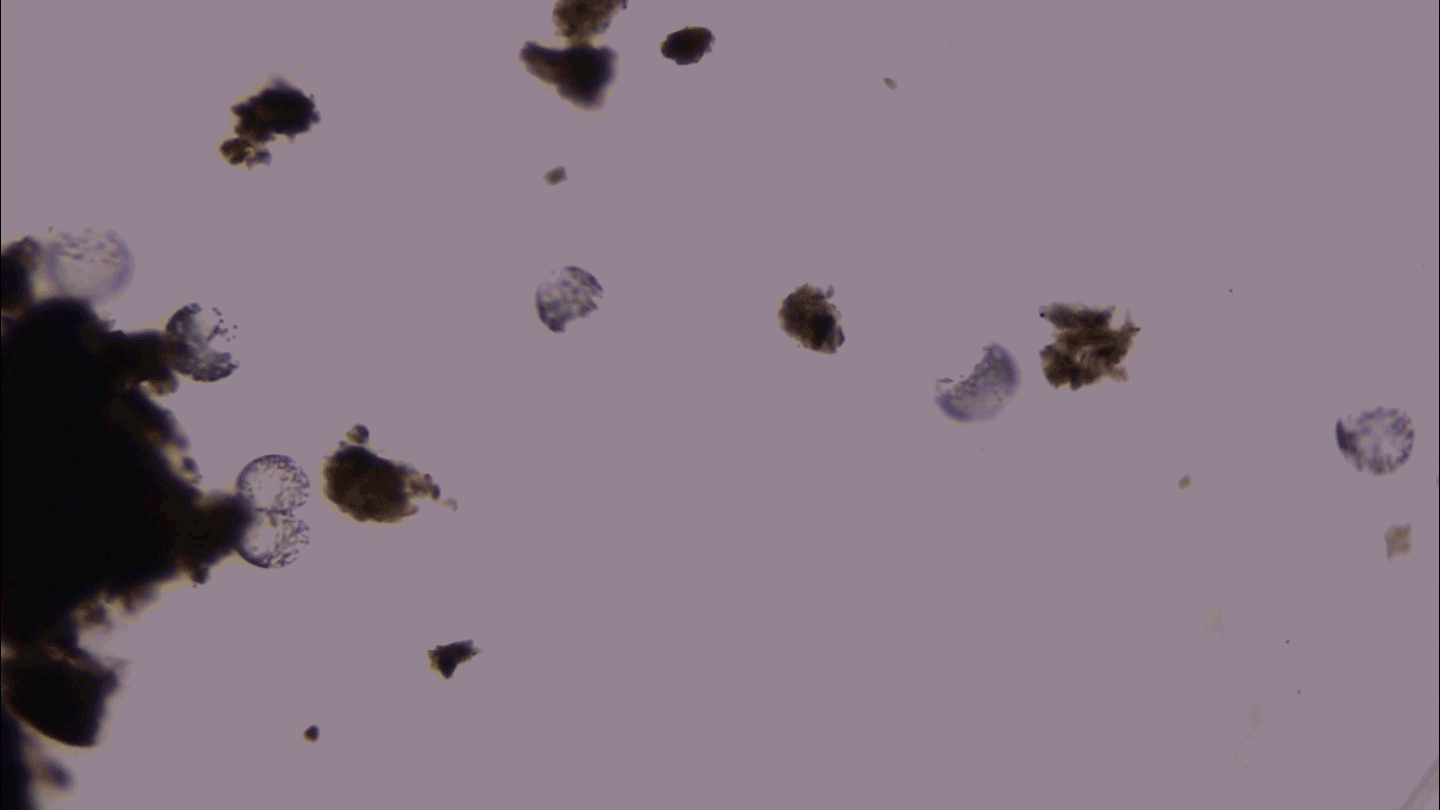 Microbes
MicrobesThis giant microbe organizes its DNA in a surprising way
3-D microscopy shows that the giant bacterium Thiovulum imperiosus squeezes its DNA into peripheral pouches, not a central mass like typical bacteria.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGLP-1 drugs failed to slow Alzheimer’s in two big clinical trials
Tantalizing results from small trials and anecdotes raised hopes that drugs like Ozempic could help. Despite setbacks, researchers aren’t giving up yet.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSelf-hypnosis with cooling mental imagery could ease hot flashes
Postmenopausal women who listened to self-guided hypnosis recordings daily for six weeks saw meaningful improvements in hot flash symptoms.
-
 Humans
HumansA therapeutic HPV vaccine shrank cervical tumors in mice
An HPV vaccine delivered into the nose can treat cervical tumors in mice. The vaccine targets a cancer protein produced by the virus.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine3,000 steps per day might slow Alzheimer’s disease
In people at risk for Alzheimer’s disease, researchers linked minimal to moderate physical activity to a 3-to 7-year delay in cognitive symptoms.