
McKenzie Prillaman
Staff Writer
McKenzie Prillaman is a science and health journalist based in Washington, DC, who interned at Science News in spring 2023. She holds a degree in neuroscience from the University of Virginia and studied adolescent nicotine dependence at the National Institute on Drug Abuse. After figuring out she’d rather explain scientific research than conduct it, she worked at the American Association for the Advancement of Science and then earned a master’s degree in science communication from the University of California, Santa Cruz. Her work has appeared in Nature, Scientific American, The Cancer Letter and The Mercury News, among other publications.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by McKenzie Prillaman
- Planetary Science
NASA’s Webb telescope spotted a new moon orbiting Uranus
Like Uranus's other 28 moons, the newfound object spotted by JWST will be named after a William Shakespeare or Alexander Pope character.
- Astronomy
A dying star revealed its heart
Before exploding, a star shed most of its layers, giving a glimpse at a massive star’s deep interior. The event may represent a new kind of supernova.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe oldest known black hole formed more than 13.3 billion years ago
The Webb telescope found that a far-off little red dot is the oldest known black hole, shrouded by gas that could help explain the ruby color.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceCosmic rays could, in theory, sustain life on other worlds
The hypothesis could extend the search for extraterrestrial life to include frigid planets with thin atmospheres and underground water.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceA giant planet may orbit our closest sunlike neighbor
Alpha Centauri A, four light-years from Earth, may host a gas giant. If confirmed, no Earthlike planets orbit in the star’s habitable zone.
- Astronomy
Seven superclouds sit just beyond the solar system
The superclouds probably produce star-forming clouds of gas, since most nearby stellar nurseries are located within the giants.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe Webb space telescope spies its first black holes snacking on stars
These star-shredding black holes sit within dusty galaxies that block many telescopes’ views. That’s not an issue for JWST.
-
 Astronomy
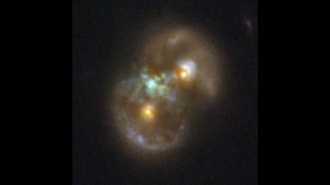
AstronomyTwo colliding galaxies may have birthed this black hole
An infinity symbol–shaped galaxy hosts an active supermassive black hole. The growing giant may have come from the aftermath of a galactic smashup.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceThis star offers the earliest peek at the birth of a planetary system like ours
A young sunlike star called HOPS 315 seems to host a swirling disk of gas giving rise to minerals that kick-start the planet formation process.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNew Horizons visited Pluto 10 years ago. We’re still learning from it
Over the past decade, researchers have been puzzling through Pluto’s mysteries. Meanwhile, the New Horizons probe heads for interstellar space.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyNearly half of the universe’s ordinary matter was uncharted, until now
Two studies fill in gaps about the cosmos’s ordinary matter. One maps it all, even the “missing matter.” The other details one of its hiding spots.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA rare chance to see two exploding stars is happening in the southern sky
Exploding stars V462 Lupi and V572 Velorum are best seen from the Southern Hemisphere. One has been spotted from the United States.