All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor glowworms, the brightest girls get the guy
Brighter female glowworms attract more mates and lay more eggs than their dimmer peers.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPentaquarks, locked-in syndrome and more reader feedback
Readers discuss pentaquark sightings, delightful diatoms and whether an ancient four-legged fossil was actually a snake.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyPerspiration is important, but inspiration is fun(damental)
How much of science is inspiration versus perspiration?
By Eva Emerson -
 Genetics
GeneticsAsian tiger mosquito genome sequenced
Researchers have sequenced the genome of the Asian tiger mosquito, a stealthy invasive species and carrier of tropical diseases.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor glowworms, the brightest girls get the guy
Brighter female glowworms attract more mates and lay more eggs than their dimmer peers.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow architecture can make ants better workers
The right nest architecture can make harvester ants better at their job, new research shows.
By Susan Milius -
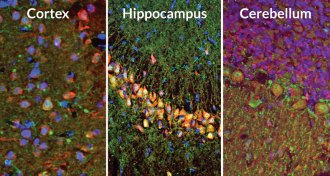 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNets full of holes catch long-term memories
Tough structures that swaddle nerve cells may store long-term memories.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSex influences ability to assess crowd’s emotion
New analyses explain how people detect an angry mob or a happy party.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHigh-fat diet’s negative effect on memory may fade
Brain may find way to compensate for memory impairments linked to high-fat diets, study in rats shows.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Paleontology
Paleontology300 million-year-old giant shark swam the Texas seas
Fossil find shows oldest known ‘supershark,’ about the size of a limo, prowled the ocean 300 million years ago.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyDead stars team up for supernova explosions
Three type 1a supernovas show hints of being triggered by collisions between pairs of white dwarfs.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHollywood-made science documentary series comes to TV
Breakthrough series gives a closer look at scientists at work.