All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyComet carries alcohol, sugar
Sugar and alcohol are just two of the ingredients that go into making a comet.
-
 Climate
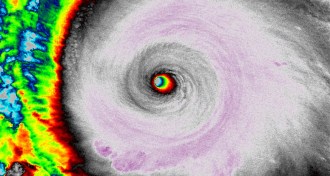
ClimateHurricane Patricia’s howling winds smash records
Hurricane Patricia’s winds are now the fastest ever recorded in a tropical cyclone, making it the strongest hurricane on record in the Western Hemisphere.
-

-
 Animals
AnimalsAs panda baby grows, mom’s milk changes
In the first month after a mama panda gives birth, her milk changes in composition, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHowler monkeys sacrifice sperm for deeper roars
In howler monkeys, expanded vocal tracts make for deeper-voiced males with smaller testes, researchers find.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSigns of Alzheimer’s seen in young brain’s GPS cells
Signs of Alzheimer’s can show up in the brain’s compass decades before symptoms strike.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
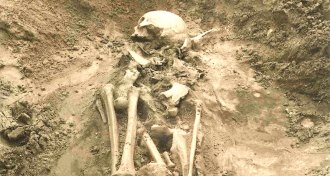
AnthropologyPlagues plagued the Bronze Age
Ancient bacterial DNA provides first clues to Bronze Age plagues in Europe and Asia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive species may be great snacks for predators
The arrival of a new food source can benefit predators, a new study finds. But if there are no native species around to eat, it’s a different story.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFurry, spiky mammal scampered among dinosaurs
Early Cretaceous fur ball with spikes discovered in Spain.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhite dwarf upsets planetary system, consumes evidence
Rocky planets are disintegrating around a white dwarf, the core of a dead star.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhite dwarf upsets planetary system, consumes evidence
Rocky planets are disintegrating around a white dwarf, the core of a dead star.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsConfirmed: Quantum mechanics is weird
The first demonstration of a loophole-free Bell test validates the weirdness of quantum physics.
By Andrew Grant