All Stories
-
 Neuroscience
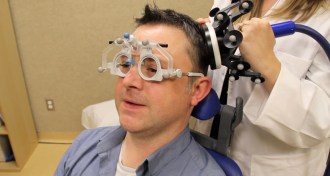
NeurosciencePulses to the brain bring memory gains
The ability to associate faces with words is boosted when an outer part of the brain is stimulated, a study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSpiders get bigger in the big city
City-living golden orb-weaving spiders tend to be bigger than those that live in the countryside, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBabies may be good at remembering, and forgetting
Studies in kids suggest that young children can form memories but can’t recall them later, offering new clues to how memory-storing systems form in young brains.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyPleiades star cluster is a bit farther away than thought
New observations might impact Gaia satellite’s mission to map the Milky Way.
-
 Genetics
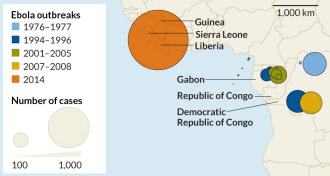
GeneticsEbola genome clarifies origins of West African outbreak
Genetic analyses suggest that a single infected person sparked the ongoing Ebola epidemic in West Africa.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologySiberians came to North American Arctic in two waves
Siberian ancestors of the modern-day Inuit replaced a 4,000-year-old North American Arctic culture, a DNA study reveals.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
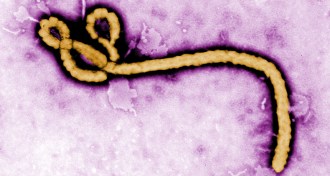
Health & MedicineHuman tests of experimental Ebola vaccine set to start
NIH and NIAID have announced that human tests of an experimental vaccine against Ebola virus will begin in early September.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTo grow new knee cartilage, look to the nose
Cartilage-making cells from the nose grew into patches that successfully replaced damaged or missing cartilage in the knees of goats and of humans.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWake of nearby supernova hints at explosion’s origins
Gamma rays from radioactive decay of cobalt formed in a nearby supernova reveal unprecedented details of the explosion’s aftermath.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyWalking in sync makes enemies seem less scary
Men who walk in sync may begin to think of their enemies as weaker and smaller, a new study suggests.
-
 Quantum Physics
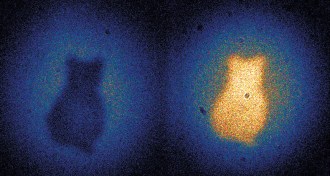
Quantum PhysicsBlind quantum camera snaps photos of Schrödinger’s cat
Quantum weirdness lets physicists snap photo without collecting incoming light from cardboard cat subject.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceLaser light rewrites memories in mice
Mouse experiment demonstrates that good memories can be transformed into bad ones, and vice versa.