
Ashley Yeager is the associate news editor at Science News. Previously, she worked at The Scientist, where she was an associate editor for nearly three years. She has also worked as a freelance editor and writer, and as a writer at the Simons Foundation, Duke University and the W.M. Keck Observatory. She was the web producer for Science News from 2013 to 2015, and was an intern at the magazine in the summer of 2008. She holds a bachelor’s degree in journalism from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, and a master’s degree in science writing from MIT. Her book, Bright Galaxies, Dark Matter and Beyond, on the life of astronomer Vera Rubin, will be published by MIT Press in August.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Ashley Yeager
-
 Genetics
GeneticsRainbow trout genome shows how genetic material evolved
The finding challenges the idea that whole genome duplications are followed by quick, massive reorganization and deletions of genetic material.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsNew antibiotic resistance genes found in cow manure
Identifying these genes offers clues to how antibiotic resistance could move from agricultural ecosystems to other communities of organisms.
-
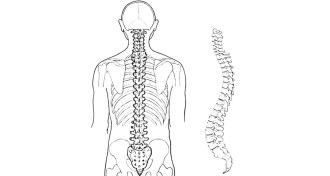 Genetics
GeneticsNeandertal, modern human DNA deviates even more
An analysis of genetic material of Neandertals and modern humans shows genetic differences in the species' population sizes and even the curves of their spines.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentLead levels in ancient Rome’s water were high, but not toxic
Ancient Romans probably drank tap water with up to 100 times more lead than the levels found in local spring water.
-
 Life
LifeInsulating sheath on nerve cells isn’t an even coat
Myelin doesn't evenly coat axons, a finding that runs counter to what scientists suspected.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGene variant, processed meat linked to boost in cancer risk
In people with a specific variation of a gene on chromosome 10, eating processed meat is associated with an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
-
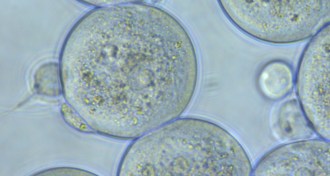 Life
LifeProtein that gets sperm into egg identified
The protein Folr4 on a reproductive egg plays this crucial role in the fusion of the sperm and egg, research shows.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEven with rest, brain changes linked to football linger
The offseason may not allow enough time for football players' brains to heal from hard hits.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly meat-eater may have led to larger plant-eaters
The newly identified Eocasea martini may have set the stage for later, much larger animals to become plant-eaters.
-
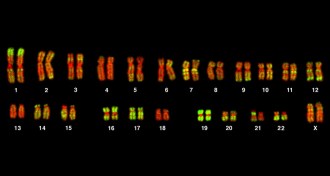 Genetics
GeneticsDown’s syndrome goes beyond chromosome 21
A genetic analysis suggests that the DNA changes linked to Down's syndrome happen on all chromosomes, not just the 21st.
-
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsExcitons’ motions captured in images
Scientists have observed how quasiparticles called excitons move.