News
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyCancer studies get mixed grades on redo tests
Replications of cancer studies fail to reproduce some results.
-
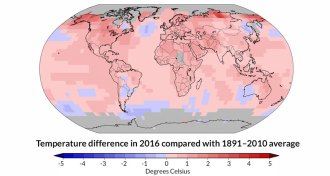 Climate
ClimateFor three years in a row, Earth breaks heat record
Spurred by climate change and heat from a strong El Niño, 2016 was the hottest year on record.
-
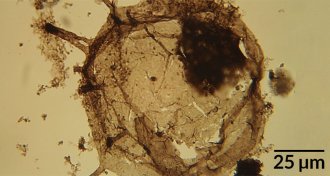 Earth
EarthCoastal waters were an oxygen oasis 2.3 billion years ago
Coastal waters contained enough oxygen to support complex life-forms including some animals hundreds of millions of years before fossils of such life first appear.
-
 Climate
ClimatePetrified tree rings tell ancient tale of sun’s behavior
The 11-year cycle of solar activity may have been around for at least 290 million years, ancient tree rings suggest.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePromise and perils of marijuana deserve more scientific scrutiny
Report outlines medical potential and health dangers of cannabis and its components.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryNew molecular knot is most complex yet
The knot is woven from 192 atoms of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen and forms a triple braid with eight crossing points.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow mice use their brain to hunt
Messages from the brain’s amygdala help mice chase and kill prey.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIt takes guts for a sea spider to pump blood
Most sea spiders have hearts, but what really gets their blood flowing are gut contractions.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeurosciencePain promoter also acts as pain reliever
A pain-sensing protein also regulates activity of pain-relieving opioids.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMany tiny moons came together to form moon, simulations suggest
Earth’s moon formed from mini-moons generated by a series of medium to large impacts, rather than from one colossal collision, researchers propose
-
 Animals
AnimalsUnusually loose skin helps hagfish survive shark attacks
Hagfish skin that easily slips and slides can be a lifesaver in crises such as shark attacks.
By Susan Milius -
 Chemistry
ChemistryDebate heats up over claims that hot water sometimes freezes faster than cold
A team of chemists has a new explanation for the Mpemba effect, while other scientists debate if it is even real.