News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimulations of your gut may predict which probiotics will stick
A “digital gut” predicted which probiotics and high‑fiber diets would take hold in people's guts and produce healthier outcomes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA rising percentage of U.S. teens aren’t getting enough sleep
Teens need eight to 10 hours of sleep each night. A large majority get less than that, according to a national survey of U.S. high school students.
-
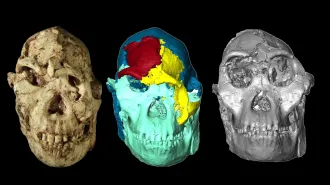 Anthropology
AnthropologyThe ancient human ancestor ‘Little Foot’ gets a new face
A new digital reconstruction of the face of an early Australopithecus specimen helps add details about the origins of our own species.
By Jay Bennett -
 Space
SpaceNASA scraps its 2027 moon landing, adds two missions in 2028
Rather than land astronauts on the moon, the Artemis III mission will now focus on docking and space suit tests in low Earth orbit.
-
 Climate
ClimateTake it from the Olympics, slushy winter sports may be the new normal
Ice arenas and artificial snow now dominate the winter Olympics. Athletes there — and everywhere — may need to adjust how they train and perform.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWhy is math harder for some kids? Brain scans offer clues
Kids with math learning disabilities process number symbols differently than quantities shown as dots — and it shows up in MRIs.
By Lily Burton -
 Animals
AnimalsHere’s how honeyeaters and other birds thrive on sugary diets
Birds that feed on nectar or fruit evolved better mechanisms for managing metabolism, blood pressure and high glucose.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMosquitoes began biting humans more than a million years ago
A DNA analysis suggests mosquitoes shifted from nonhuman primates to early humans nearly 2 million years ago.
By Tom Metcalfe -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan you trust the results from gut microbiome tests? Maybe not
Seven firms reported inconsistent results on the same sample, some over multiple tests. These gut microbe discrepancies could have health consequences.
- Animals
Climate change could threaten monarch mass migration
Suitable milkweed habitat in Mexico may shift south, fracturing existing migration routes and possibly pushing some butterflies to stay put.
-
 Earth
EarthMetal pollution from a rocket reentry detected for the first time
Direct detection of lithium from a SpaceX rocket reentry offers new evidence that metal pollution from space debris could threaten the ozone layer.
By Adam Mann -
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s why sneakers squeak on the basketball court
Tiny, repeating detachments between sole and floor — thousands of times a second — create the distinctive squeak heard on the court, data show.