How a bacterial toxin linked to colon cancer messes with DNA
Colibactin has “warheads” that seek and destroy DNA

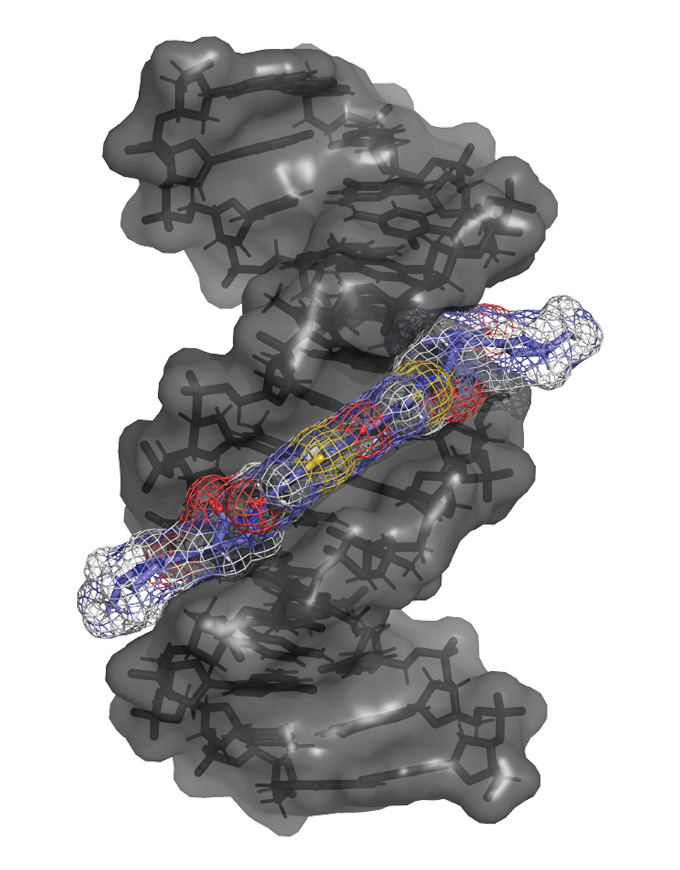
Some gut bugs make the DNA-altering toxin colibactin, which sticks to and damages DNA by bridging the two strands of the double helix, as illustrated here. The mutations it leaves behind are linked to colon cancer. A new study explains where and how colibactin does its damage.
DEMCON | nymus3D, ©Hubrecht Institute
This is a human-written story voiced by AI. Got feedback? Take our survey . (See our AI policy here .)