Video
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
- Astronomy
A dying star revealed its heart
Before exploding, a star shed most of its layers, giving a glimpse at a massive star’s deep interior. The event may represent a new kind of supernova.
-
 Space
SpaceAstronauts need oxygen. Magnets could help
Adding a magnet could simplify the process of producing oxygen in space, making a crewed mission to Mars more feasible.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA single protein makes lovesick flies spill their guts
Producing a male-specific protein in digestion-related neurons may have led to the evolution of an odd “romantic” barfing behavior in one species of fruit flies.
- Environment
See how aerosols loft through Earth’s sky
Aerosols, small particles in the atmosphere like salt and dust, may offset a third of human-caused climate warming, though their influence is fading.
By Nikk Ogasa -
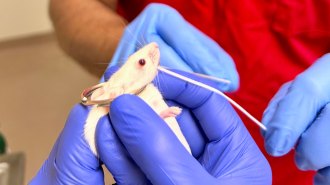 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow flossing a mouse’s teeth could lead to a new kind of vaccine
Flu viruses often enter the body through mucous tissue in the nose. Researchers are developing new ways to protect such areas.
-
 Plants
PlantsThese plants build ant condos that keep warring species apart
The unique architecture of some ball-like plants high in trees in Fiji lets violent ants live peacefully and feed the plant with valuable droppings.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsSome killer whales hunt in pairs to maximize their bounty
Drone footage from Norway shows killer whales using a highly coordinated and cooperative hunting technique to catch herring.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA dog’s taste for TV may depend on its temperament
Anxious dogs might react nervously to some television sounds, a survey of dog owners reports, while hyper ones might try to play chase.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHow fast did dinosaurs really go? Birds walking in mud provide new clues
Tracks of dinosaur footprints can hint at how fast the extinct animals moved. Here’s how guinea fowl can help fact-check those assumptions.
-
 Animals
AnimalsKiller whales may use kelp brushes to slough off rough skin
The whales use quick body movements to tear pieces of bull kelp for use as tools, perhaps the first known toolmaking by a marine mammal.
-
 Animals
AnimalsU.S. seal populations have rebounded — and so have their conflicts with humans
Alix Morris’s new book, A Year with the Seals, explores humans’ complicated relationship with these controversial marine mammals.
-
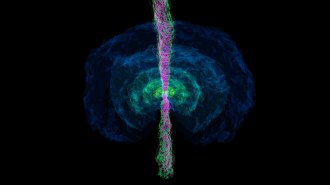 Space
SpaceHere’s how a collision of star remnants launches a gleaming jet
A computer simulation shows how two neutron stars of unequal mass merge, form a black hole and spit out a jet of high energy matter.