Search Results for:
Skip to resultsCan’t find what you’re looking for? Visit our FAQ page.
113,039+ results for:
- Artificial Intelligence
Have we entered a new age of AI-enabled scientific discovery?
Some say we’ve entered a new age of AI-enabled scientific discovery. But human insight and creativity still can’t be automated.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists dream up ‘spacetime quasicrystals’ that could underpin the universe
Quasicrystals are orderly structures that never repeat. Scientists just showed they can exist in space and time.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome snakes lack the ‘hunger hormone.’ Experts are hungry to know why
The complex biology of ghrelin, the hunger hormone, has researchers wondering how its absence helps snakes last a long time with no food, if at all.
By Andrea Lius -
 Tech
TechThe Story of Stories traces the arc of storytelling across human history
In The Story of Stories, technologist Kevin Ashton explores how storytelling has evolved and why stories matter.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceReal-world medical questions stump AI chatbots
Subtle shifts in how users described symptoms to AI chatbots led to dramatically different, sometimes dangerous medical advice.
-
 Oceans
OceansEvolution didn’t wait long after the dinosaurs died
New plankton arrived just a few millennia — maybe even decades — after the Chicxulub asteroid, forcing a rethink of evolution's catastrophe response speed.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Animals
AnimalsA sea turtle boom may be hiding a population collapse
In Cape Verde, conservation has boosted the sea turtle population 100-fold — but the male-female balance is way off.
-
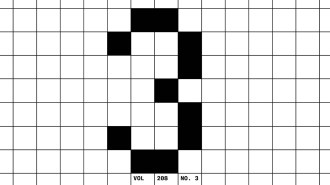
Crossword: Copy That!
Solve the crossword from our March 2026 issue, in which we work on our code-switching.
By Rena Cohen -
 Astronomy
AstronomyThis inside-out planetary system has astronomers scratching their heads
A rocky exoplanet in the LHS 1903 system defies planet formation models, hinting that gravitational upheaval reshaped the red dwarf’s four worlds.
By Adam Mann -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA simple shift in schedule could make cancer immunotherapy work better
A lung cancer trial bolsters a long-held idea that treatment timing matters, showing a simple shift could help immunotherapy work better and extend lives.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis baby sling turns sunlight into treatment for newborn jaundice
A student created a low-cost baby carrier that filters sunlight to safely treat jaundice where electricity and equipment are scarce.
By Elie Dolgin -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsFood chains in Caribbean coral reefs are getting shorter
Shorter food chains could mean reefs are less able to weather changes in food availability, threatening an already vulnerable ecosystem.