Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeBird plus goggles equals new insight into flight physics
Slow-flying parrotlet produces vortices that explosively break up.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFirst spider superdads discovered
Male spiders first known to give up solitary life for offspring care, often as a single parent.
By Susan Milius -
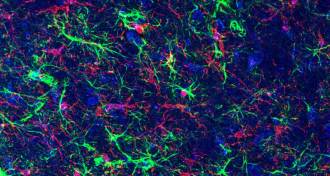 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGut microbe mix may spark Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s disease symptoms might be driven by gut microbes
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryEnzyme forges carbon-silicon bonds with a little human help
A few tweaks to an enzyme help it link carbon to silicon — a match not found in nature.
-
 Life
LifePublic, doctors alike confused about food allergies
Gaps in understanding food allergies cause confusion and make it difficult to prevent, diagnose and treat them.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyScientific success depends on finding light in darkness
Editor in chief Eva Emerson discusses using cleverness and persistence to uncover scientific truths.
By Eva Emerson -
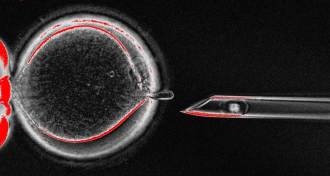 Life
LifeMitochondria variants battle for cell supremacy
Some mitochondria are more competitive than others, which could complicate treatments for mitochondrial diseases.
-
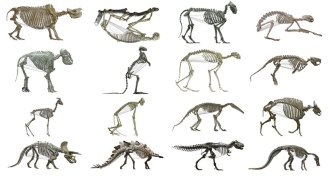 Animals
AnimalsPlant-eating mammals sport bigger bellies than meat eaters
Mammalian plant eaters have bigger torsos than meat eaters, a new analysis confirms, but the same might not have held true for dinosaurs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAnimals give clues to the origins of human number crunching
Guppies, dogs, chickens, crows, spiders — lots of animals have number sense without knowing numbers.
By Susan Milius -
 Oceans
OceansCoral die-off in Great Barrier Reef reaches record levels
Bleaching has killed more than two-thirds of corals in some parts of the Great Barrier Reef, scientists have confirmed.
-
 Life
LifeBlue leaves help begonias harvest energy in low light
The iridescent color of some begonias comes from tiny structures that also help the plant convert dim light into energy.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesCut leaves in bagged salads help Salmonella grow
Juice from torn-up leafy greens helps Salmonella spread in bagged salads.