Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLow social status leads to off-kilter immune system
Low social status tips immune system toward inflammation seen in chronic diseases, a monkey study shows.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDogs form memories of experiences
New experiments suggest that dogs have some version of episodic memory, allowing them to recall specific experiences.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNow there are two bedbug species in the United States
The tropical bedbug hadn’t been seen in Florida for decades. Now scientists have confirmed it has either resurfaced or returned.
-
 Plants
PlantsBacteria help carnivorous plants drown their prey
Pitcher plant drowning traps are more difficult for an insect to escape when bacteria colonize them.
By Susan Milius -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyCretaceous bird find holds new color clue
New molecular clues in 130-million-year-old bird fossil could help paleontologists firm up case for ancient color in dinosaurs.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsBrazilian free-tailed bats are the fastest fliers
Ultrafast flying by one bat species leaves birds in the dust.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAn echidna’s to-do list: Sleep. Eat. Dig up Australia.
Short-beaked echidna’s to-do list looks good for a continent losing other digging mammals.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsTweaking how plants manage a crisis boosts photosynthesis
Shortening plants’ recovery time after blasts of excessive light can boost crop growth.
By Susan Milius -
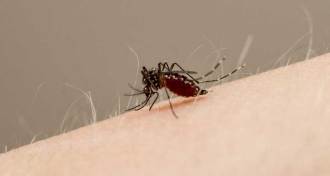 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: Vaginal vulnerability, disease double trouble and more
Puerto Rico cases of Zika suggest that the virus prefers women. And two new findings reveal more about Zika’s transmission and ability to survive outside the body.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsIn some ways, hawks hunt like humans
Raptors may track their prey in similar patterns to primates.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDespite Alzheimer’s plaques, some seniors remain mentally sharp
Plaques and tangles riddle the brains of some very old and very healthy people.
-
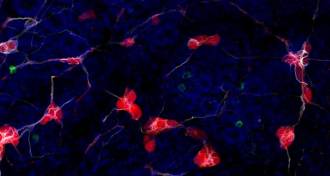 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProtein linked to Parkinson’s travels from gut to brain
Parkinson’s protein can travel from gut to brain, mouse study suggests.