Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeBritish red squirrels serve as leprosy reservoir
Red squirrels in the British Isles can harbor the bacteria that cause leprosy.
-
 Life
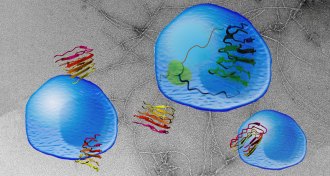
LifeProtein mobs kill cells that most need those proteins to survive
A protein engineered to aggregate gives clues about how clumpy proteins kill brain cells.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGiggling rats help reveal how brain creates joy
Rats relish a good tickle, which activates nerve cells in a part of the brain that detects touch.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDragon dinosaur met a muddy end
‘Mud dragon’ fossil discovered in China suggests that dinosaurs’ last days were an active time of evolution.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsOld bonobos have bad eyesight — just like us
As bonobos age, they lose their ability to see things close up, a new study suggests.
-
 Climate
ClimateCO2-loving plants can counter human emissions
Plants temporarily halted the acceleration of rising carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, new research suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMost illegal ivory is less than three years old
Most of the ivory seized by law enforcement in the last decade doesn’t come from elephants poached many years ago.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMost illegal ivory is less than three years old
Most of the ivory seized by law enforcement in the last decade doesn’t come from elephants poached many years ago.
-
 Tech
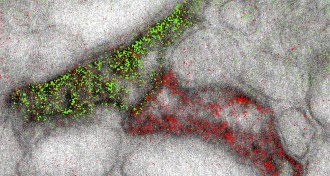
TechNew technique shows cells’ molecules in color
A new electron microscopy technique reveals cellular details in multicolor
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShape-shifting molecule aids memory in fruit flies
A prionlike protein may store long-term memories in fruit flies, a new study suggests.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCancer mutation patterns differ in smokers, nonsmokers
The DNA of smokers shows more damage than the DNA of nonsmokers who have the same kind of cancer.
-
 Life
LifeCity dolphins get a boost from better protection and cleaner waters
Bottlenose dolphins near Adelaide, Australia, are slowly growing in number due to better environmental conditions and better protection.