Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years later, vaccines have eliminated some diseases
Vaccines have come a long way in 50 years.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyReaders unimpressed by Earth’s newest neighbor
Exoplanet fatigue, runaway fish and more in reader feedback.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene gives mice and chipmunks their pinstripes
A recycled regulator paints on rodents’ light stripes.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenetic variant protects against rash of autoimmune diseases
A natural tweak in the TYK2 protein strikes a balance between weak and overactive immune systems.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsProtective genetic variant may offer a path to future autoimmune therapies
A natural tweak in the TYK2 protein strikes a balance between weak and overactive immune systems.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEyes offer window into brain’s timekeepers
In new experiments of time perception, when pupils were large, monkeys underestimated a second.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFirst known fossilized dinosaur brain unearthed, scientists claim
A dinosaur fossil that preserves brain tissue has been discovered for the first time, researchers announce.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPicture of primate common ancestor coming into focus
A new family tree analysis predicts behavior of primate common ancestor.
By Erin Wayman -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly birds could achieve liftoff
Early birds and other flying dinosaurs had the strong legs and wing speed needed to launch into the air directly from the ground, researchers argue.
By Meghan Rosen -
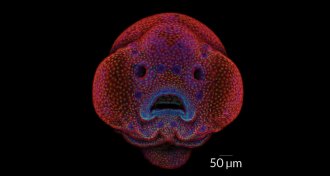 Life
LifeHow to make a fish face, and other photo contest winners
The tiny face of a 4-day-old zebrafish embryo snags the top spot in microscopy photography contest.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient hookups gave chimps a smidge of bonobo DNA
Genetic evidence suggests bonobos and chimpanzees interbred after becoming separate species.
-
 Life
LifeScientists need to redraw picture of cell’s biggest organelle
A close-up view of the cell’s endoplasmic reticulum reveals a different structure.