Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change shifts how long ants hang on to coveted real estate
Simulated climate warming reveals a new pattern in turnover of ant nests.
By Susan Milius -
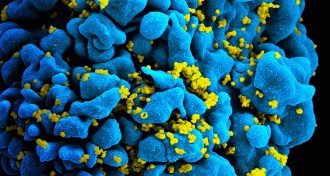 Genetics
GeneticsHIV came to NYC at least a decade before virus ID’d
DNA analysis of early viral strains tracks U.S. debut to early ’70s
-
 Animals
AnimalsWith climate change, grizzly bears may hibernate less
New research shows that food availability and weather are driving when grizzly bears enter and exit their dens for hibernation.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFrequent liars show less activity in key brain structure
Brain activity changed as people lied more, a new study finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA data offer evidence of unknown extinct human relative
Melanesians may carry genetic evidence of a previously unknown extinct human relative.
-
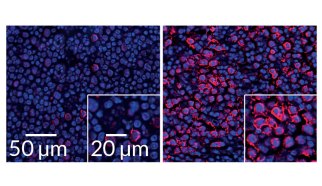 Life
LifeVirus triggers immune proteins to aid enemy
Virus-fighting proteins in the immune system can sometimes help out their targets instead.
-
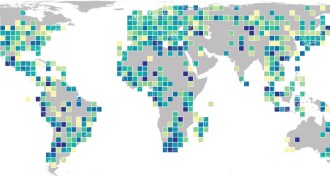 Animals
AnimalsMaps show genetic diversity in mammals, amphibians around the world
Maps of genetic diversity within mammal and amphibian species provide a baseline for understanding the effects of human activity and climate change on animals.
By Kate Travis -

-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient armored fish revises early history of jaws
The fossil of a 423-million-year-old armored fish from China suggests that the jaws of all modern land vertebrates and bony fish originated in a bizarre group of animals called placoderms.
By Meghan Rosen -
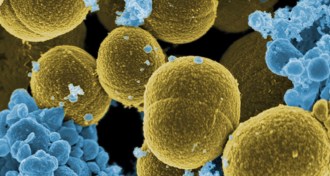 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStaph infections still a concern
Scientists have been searching for a vaccine against a deadly microbe for 50 years.
-
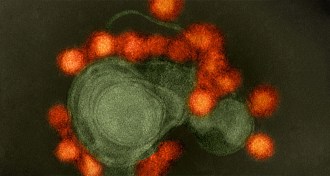 Genetics
GeneticsZika disrupts cellular processes to impair brain development
Discoveries about how Zika virus slows brain cell development could lead to treatments.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsReaders question the biology of alcoholism and more
Alcoholism-linked genes, making better corneas and more in reader feedback.