Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWith Tasmanian devils gone, possums come down from the trees
In areas where Tasmanian devils have largely disappeared, their prey is becoming more adventuresome, a new study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
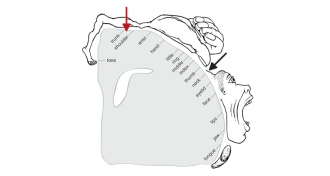
NeuroscienceHomunculus reimagined
A new study pinpoints the part of the brain that controls the neck muscles, tweaking the motor homunculus.
-
 Neuroscience
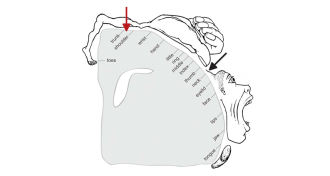
NeuroscienceHomunculus reimagined
A new study pinpoints the part of the brain that controls the neck muscles, tweaking the motor homunculus.
-
 Animals
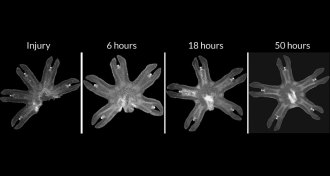
AnimalsMoon jellies muscle their way to recovery
Symmetrization, using rapid muscle movements to repair body symmetry, is the go-to healing mechanism for the limbed stage of moon jellyfish.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMale peacocks keep eyes low when checking out competition
Eye-tracking technology shows peacocks barely gaze at the full height of other males magnificent eyespot feather spreads.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsHow a trap-jaw ant carries a baby
Powerful jaws make the Odontomachus brunneus ant a skilled escape artist.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy whistling caterpillars scare birds
Caterpillars that whistle when birds peck at them may be giving phony avian warning calls.
By Susan Milius -
 Microbes
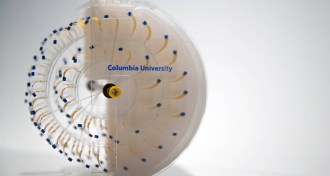
MicrobesSpore-powered engines zoom ahead
Engines that run on the dehydration of bacterial spores can power a tiny car and an LED.
By Beth Mole -
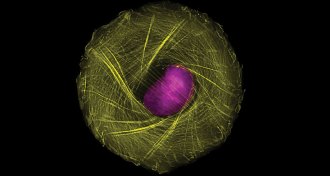 Life
LifeTwisty chains of proteins keep cells oriented
The counterclockwise twist of protein fibers jutting out from the edge of human cells allow the cells to distinguish right from left.
-
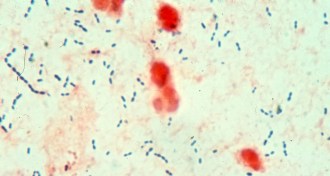 Genetics
GeneticsPneumonia bacteria attacks lungs with toxic weaponry
Some strains of the bacteria that causes pneumonia splash lung cells with hydrogen peroxide to mess with DNA and kill cells, a new study suggests.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsOcean food source lives by day, dies by night
The most abundant carbon fixer in the oceans lives by day, dies by night, and may be key to the balance of marine ecosystems.
-
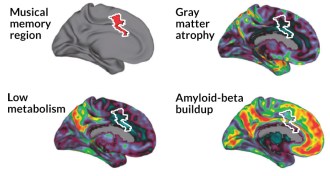 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAlzheimer’s spares brain’s music regions
Brain regions involved in recognizing familiar songs are relatively unscathed in Alzheimer’s disease.