Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
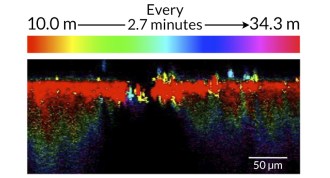
LifeTracing molecules’ movement in nails may help fight fungus
Tracking chemicals through the human nail may provide valuable insight for drug development.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyHorned dino aside, here are some other fun fossil finds
Here's a roundup of some fossil finds reported this week.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Virgin births’ won’t save endangered sawfish
Sawfish are the first wild vertebrates found to reproduce via parthenogenesis.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFemale’s nose blocks scent of a male
When a female mouse is in an infertile stage of her reproductive cycle, her nose cells don’t alert her brain to the presence of a potential mate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFly spit protein holds back parasite infection in monkeys
A protein called PdS15 found in the saliva of the sand fly that spreads leishmaniasis may be used in a vaccine to combat the parasitic scourge causing the illness.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyTriceratops relative reveals dino diversity
A newly discovered relative of Triceratops provides new insight into the evolution of horned dinosaurs.
-
 Genetics
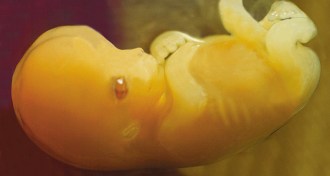
GeneticsDNA tags mostly deleted in human germ cells
Human embryos come with some heavy-duty erasers. Chemical tags on DNA get mostly wiped out in the womb.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsPregnant male pipefish not so great at giving embryos oxygen
During male pregnancy, pipefish embryos can get stunted by low oxygen in dad’s brood pouch.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsAfrican herbivores share space but not diet
Large herbivorous mammals on the plains of Kenya have distinctive diets, a new study finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
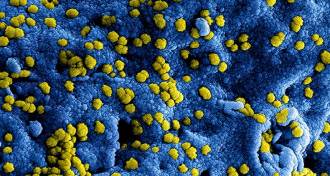
Health & MedicineDeadly MERS spreads in small cluster in South Korea
Thirty people have MERS virus in the South Korean outbreak, including China’s first case.
-

-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyChimps prefer roasted potatoes, hinting at origins of cooking
Chimps really dig roasted potatoes, suggesting cooking arose millions of years ago.
By Bruce Bower