Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHa! The Science of When We Laugh and Why
Scott Weems, a neuroscientist, takes readers on a wide-ranging tour that explains what humor is and why readers should care.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
AnimalsAs their homes warm, salamanders shrink
Many species of salamanders respond to climate change by getting smaller.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGiant pandas like sweets, but prefer the natural ones
Despite sustaining themselves on bamboo, which isn't very sweet, giant pandas will indulge in a bit of sugar, if they can.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBats’ dinner conversation may go over your head
Hunting big brown bats do more than echolocate. When male bats compete for a single prize, they send social calls to keep other bats at bay.
-
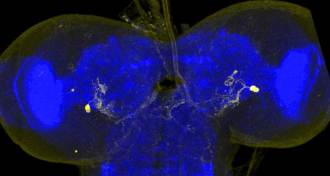 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTen thousand neurons linked to behaviors in fly
By studying the wiggles of 37,780 fly larvae, scientists link specific neurons to 29 distinct behaviors.
-
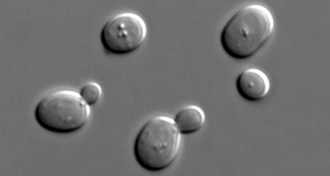 Life
LifeFirst chromosome made synthetically from yeast
Work with yeast marks the first time scientists have synthesized a chromosome from organisms with complex cells and represents a major step toward lab-created eukaryotic life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDiet fix eases Huntington’s symptoms in mice
Supplement improves health of rodents with mutation that causes neurodegeneration like that seen in Huntington’s disease.
-
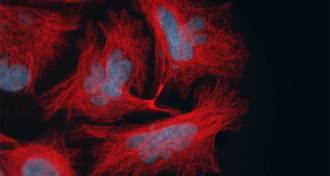 Life
LifeWith Taxol, chromosomes divide and get conquered
New mechanism discovered for how the cancer drug Taxol works.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient oceans’ top predator was gentle filter feeder
New fossils suggest that a distant relative of lobsters used bristled limbs to net its prey, not spike it.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSkewed gender ratios turn bird world into a soap opera
Infidelity, divorce and polygamy become more common among birds when one sex is rarer and has more choice in partners.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceScans suggest how the mind solves ethical dilemmas
Brain scans suggest how the mind solves a moral dilemma.
-
 Life
LifeWhen hummingbirds fly unfriendly skies
Hummingbirds hover easily in turbulent air as long as the disturbances aren’t too wide.
By Susan Milius