All Stories
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMath-anxious brains tackle simple problems differently
An fMRI study found more variable brain activity in people who get nervous about math problems.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPalace remains in Mexico point to ancient rise of centralized power
An ancient royal structure gets new life in southern Mexico.
By Bruce Bower -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsMillions of atoms entangled in record-breaking quantum tests
Scientists make advance in the quest to take quantum effects to larger scales.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMost Americans like science — and are willing to pay for it
Americans drastically overestimate how much the government spends on science. But when correctly informed, they want the government to spend more.
-
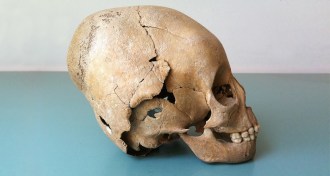 Archaeology
ArchaeologyAncient Romans may have been cozier with Huns than they let on
Nomadic Huns and Roman farmers shared ways of life on the Roman Empire’s fifth century frontier.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
EarthDeadly New Zealand quake hopscotched across faults
The Nov. 14, 2016, earthquake in New Zealand was much larger than thought possible at the time, prompting a rethink of hazard assessments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDengue fever spreads in a neighborly way
Individual strains of dengue spread locally, and new infections cluster near the home of the first person affected.
-
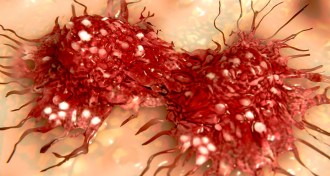 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRandom mutations play large role in cancer, study finds
Mistakes made while copying DNA account for more mutations in cancer cells than environment or inheritance do.
-
 Climate
ClimateArctic sea ice hits record wintertime low
Warm temperatures and heat waves reduced sea ice extent in the Arctic to its smallest maximum extent ever seen.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceIt’s time to redefine what qualifies as a planet, scientists propose
Astronomers can have their definition of a planet, but some planetary scientists plan to stick to the long-held meaning of the word.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsIn 1967, LSD was briefly labeled a breaker of chromosomes
Claims that the hallucinogenic drug damaged DNA were quickly rejected. But questions remain about how LSD works.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsFemale guppies with bigger brains pick more attractive guys
A larger-brained female guppy may pick primo males, but all that mental machinery costs her in other ways.
By Susan Milius