All Stories
-
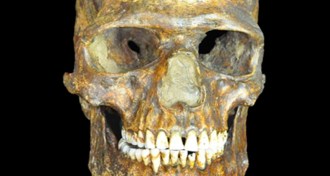 Humans
HumansYear in review: Old humans reveal secrets
DNA of the oldest modern humans is rewriting the prehistories of Europe, Siberia and the Americas.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceYear in review: Rosetta mission hits its target
The Rosetta spacecraft and its lander Philae are providing an intimate look at the life of comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko.
-
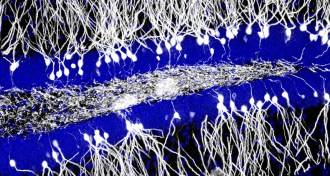 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Memories vulnerable to manipulation
New experimental results in 2014 helped bring scientists closer to understanding how the brain manipulates memories to make sense of the world.
-
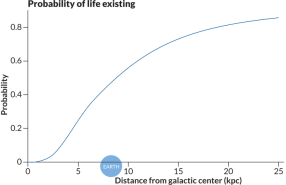 Astronomy
AstronomyGamma-ray bursts may repeatedly wipe out life
Brief bursts of high-energy radiation may sterilize most planets across the universe, hampering the chances for widespread intelligent life.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceRover finds methane in Mars air, organics in rocks
NASA’s Curiosity rover has found organic molecules on Mars, but scientists can’t say whether they are a sign of life on the Red Planet.
By Erin Wayman -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCocoa antioxidant sweetens cognition in elderly
Very high doses of antioxidants found in cocoa may prevent some types of cognitive decline in older adults. But that’s not an excuse to eat more chocolate.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyYear in review: Kepler gets second chance at life
This year, Kepler engineers figured out how to stabilize the almost-defunct Kepler telescope, while astronomers found hundreds more worlds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYear in review: Risks of e-cigarettes emerge
Electronic cigarettes dispense water vapor laced with flavors and often a hefty dose of nicotine. These vapors may be far from benign, studies in 2014 suggested.
By Janet Raloff -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: Young blood aids old brains
Ingredients in young blood can rejuvenate old mice’s bodies and brains, scientists reported in 2014.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYear in review: Gut reacts to artificial sweeteners
Saccharin messes with the body’s ability to metabolize fuel, a condition that often precedes diabetes, obesity and other metabolic problems.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDomestication did horses no genetic favors
Horses bear the cost of domestication in the form of harmful genetic variants, a study of equine DNA finds.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceYear in review: Tectonics active on Europa
Jupiter’s frozen moon Europa has a shifting exterior analogous to Earth’s plate tectonics.