All Stories
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsIt’s almost time to get to know the Higgs boson better
The next run of particle collisions at the Large Hadron collider will examine details about how the Higgs boson interacts with other particles to search for clues to new physics.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineJunk food ahead of pregnancy may harm baby-to-be
Women who have poor diets in the year before conception might have a higher risk of delivering a baby preterm than do women who eat healthful foods
By Nathan Seppa -
 Astronomy
AstronomyGalaxy seed found from 3 billion years after Big Bang
A still-growing core of a galaxy in the early universe may help astronomers understand how massive elliptical galaxies get their start.
-
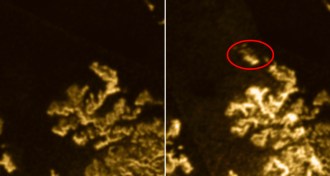 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMystery patch found floating on Titan’s seas
Changes on the surface of a methane lake on one of Saturn’s moons may signal the onset of summer there.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsElectrons’ magnetic interactions measured
Using characteristics of quantum mechanics, the minuscule magnetic interaction between two electrons has been measured.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFish-eating spiders are the stuff of nightmares
Spiders that feast on fish can be found on every continent but Antarctica, a new review finds.
-

Tiny galaxies had big influence on early universe
Nearly one-third of stars in the early universe were created in dwarf galaxies.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPassenger pigeon population had booms and busts
DNA says the birds recovered from hard times — until people came along.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeAutoimmune diseases stopped in mice
Reprogramming immune cells may offer a way to treat autoimmune diseases without harming the body’s ability to fight infections.
-
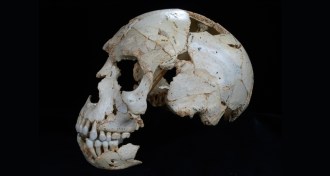 Humans
HumansSkulls reveal Neandertal’s hodge-podge genealogy
A new analysis of ancient hominid skulls reveals a patchy anatomical start of the Neandertal lineage.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsCommercial quantum computer fails to impress in new test
Fifteen million dollar D-Wave machine runs no faster than traditional computer in head-to-head challenge.
By Andrew Grant -
 Cosmology
CosmologyPaper reporting primordial gravitational waves published
The paper reporting the detection of primordial gravitational waves from a split-second after the Big Bang has finally been published.