All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePregnant women on the hook for calculating risks, benefits of fish
New draft FDA guidelines on fish for pregnant or nursing women make women do the math for how to maximize omega-3 fatty acids and minimize mercury exposure.
-
 Psychology
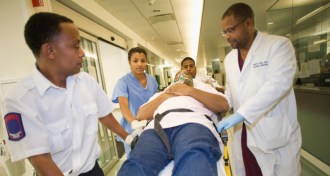
PsychologyJust four questions can identify which ER patients need prompt care
A simple decision tree may find serious ailments in ER patients’ fuzzy complaints.
By Bruce Bower -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSunbathing may boost endorphins in the body and brain
UV light makes mice churn out a molecule that is a cousin of morphine and heroin, a finding that may explain why some people seek out sunshine.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentTriclosan may spoil wastewater treatment
Common antimicrobial could make microbes more drug resistant and less efficient at breaking down sewage sludge in municipal treatment plants.
By Beth Mole -
 Physics
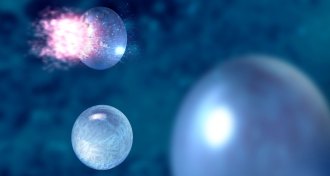
PhysicsSupercooled liquid water hits record low
Weird supercooled water well below its freezing point viewed with ultrafast laser.
By Andrew Grant -
 Astronomy
AstronomyRosetta spacecraft is closing in on comet 67P/C-G
The Rosetta spacecraft is still on track to pull up and park next to comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko in August.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSimple blood test detects heart transplant rejection
Heart transplant recipients whose bodies are starting to reject the new organ might carry genetic warning signs.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsGene variant tied to diabetes in Greenlanders
Greenlanders who carry two copies of a newly discovered gene variant have upwards of 10 times the chance of developing type 2 diabetes.
-
 Math
MathIf the world is a computer, life is an algorithm
Cellular automata may offer the algorithmic power to mimic the laws of physics and the evolution of life.
-
 Neuroscience
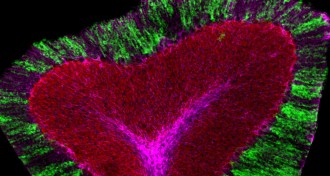
NeuroscienceStress hormone kicks brain cells into gear
Norepinephrine, a stress hormone, wakes up cells called astroglia, possibly shifting brain into vigilant state.
-
 Tech
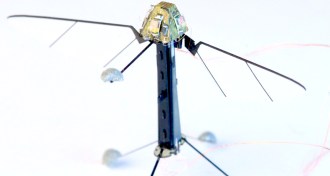
TechRobo-fly steadies flight with onboard sensor
Scaling a robot to the size of a fly and stabilizing its flight with onboard sensors offers clues to how live insects stay steady in mid-air.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyChildren negotiate taking turns surprisingly early in life
Five-year-olds can coordinate decisions with others in a fair way, even when each child has conflicting interests.
By Bruce Bower