All Stories
-
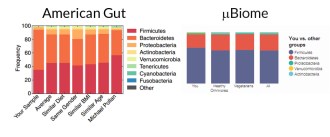 Life
LifeHere’s the poop on getting your gut microbiome analyzed
One Science News writer donated her used toilet paper for science and learned that microbiome research is as uncharted as the Wild West.
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn emergencies, fire ants get lots of grips to form rafts
First look inside fire ant architecture shows how lots of leg grips assemble rafts, bridges and balls.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsHow you bet is affected by your genes
When betting, people's decisions are influenced by variations in a set of genes that regulate the brain chemical dopamine.
-
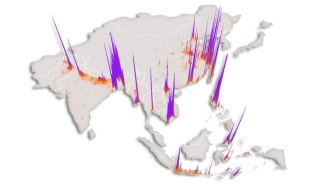 Life
LifeAvian flu could strike Asian poultry markets outside China
H7N9 influenza has a higher chance of spreading to humans in urban areas close to water, researchers predict.
-
 Animals
AnimalsMosses hitch rides on the wings of birds
Seeds may travel from far north to south hidden in the feathers of migratory birds.
-
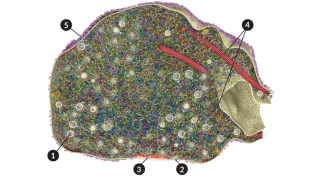 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceVisualization offers view of a nerve cell’s dispatch center
To get a closer look at how messages move in the brain, researchers created a 3-D visualization that provides a clearer view of how nerve cells communicate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUlcer microbe changes quickly to avoid immune attack
During the initial weeks of infection, Helicobacter pylori, the bacterium that causes stomach ulcers, mutates at a high rate, apparently to evade the body’s defenses.
By Nathan Seppa -
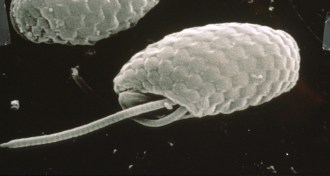 Life
LifeGenetic mutation quenches quantum quirk in algae
Studying algae that can and cannot use quantum coherence to harvest light could lead to better organic solar cells and quantum-based electronic devices.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentE-cigarettes may inflame lungs as much as cigarettes do
Acute lung impacts of e-cigarettes and tobacco cigarettes are nearly identical, new study finds.
By Janet Raloff -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeurons pull together as a brain learns
Learning and memory in rats is linked with increases in cortical oscillations, or brain cells firing off in groups, a new study shows.
-
 Physics
PhysicsEnergy-efficient laser works at room temperature
A room-temperature polariton laser, which requires little electricity, could improve electronics and medical devices.
By Andrew Grant -
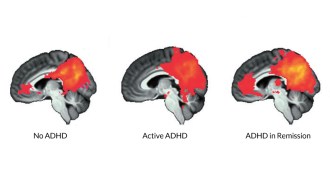 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain signal reappears after ADHD symptoms fade
In adults who no longer have ADHD, brain synchrony appears.