All Stories
-
 Life
LifeTo do: Exhibits to explore in the U.S. and London
Highlights include the impending arrival of a T. rex skeleton in Washington, D.C., a pterosaur exhibit coming to New York City, and the history of longevity at the Royal Society in London.
-
 Materials Science
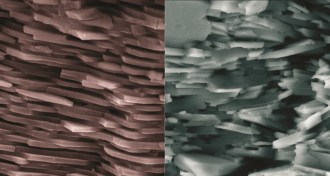
Materials SciencePearl coating inspires tougher ceramics
A material called mother of pearl, or nacre, has inspired the design of more durable, less brittle ceramics.
-
 Climate
ClimateNatural climate shifts affect sea level rise
A recent dip in the rate of sea level rise may be due to natural climate variability.
-
 Tech
TechEnglish Channel tunnel
First proposed in 1802 as a tunnel for horse-drawn carriages, the Channel Tunnel, or Chunnel, was built starting in 1987 and opened in 1994.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyCosmic question mark
Two ways of measuring the universe’s expansion rate disagree by about 10 percent. One of the methods may be flawed. Or it could be that a hitherto unobserved phenomenon is at work.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSudden death
Cardiologists disagree on whether electrocardiograms should be used to screen student athletes for a rare heart condition that can cause them to die suddenly and without warning.
By Laura Beil -
 Climate
ClimateKangaroo gut microbes make eco-friendly farts
Understanding kangaroos’ low-methane flatulence could help researchers lower greenhouse gas emissions from livestock.
By Beth Mole -
 Cosmology
CosmologyTop 10 cosmological discoveries
The cosmic microwave background radiation has played a part in many of cosmology’s greatest discoveries.
-
 Health & Medicine
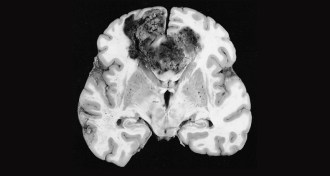
Health & MedicineSmall molecule makes brain cancer cells collapse and die
A small molecule, Vacquinol-1, may provide a different way to target and kill cells in glioblastomas, a type of brain tumor.
-
 Plants
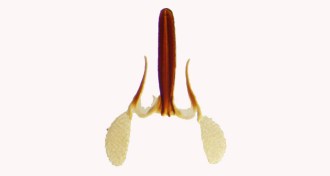
PlantsMilkweed ‘horns’ may equal wins in reproduction battle
Plants may be ripping a page right from bucks’ playbooks, developing hornlike weapons to improve their chances of reproduction.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA parasitic cuckoo can be a good thing
Great spotted cuckoo chicks show that brood parasites may benefit their hosts.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
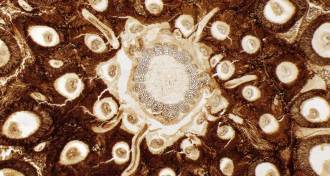
PlantsFossil fern showcases ancient chromosomes
Fossil nuclei and chromosomes seen in a 180-million-year-old fern reveals that the plants have stayed mostly the same.
By Meghan Rosen