News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyA protogalaxy in the Milky Way may be our galaxy’s original nucleus
Millions of ancient stars spanning about 18,000 light-years at the Milky Way’s heart are the kernel around which the galaxy grew, researchers say.
By Ken Croswell -
 Animals
AnimalsDrumming woodpeckers use similar brain regions as songbirds
Woodpeckers drum on trees and other objects using brain regions similar to those that songbirds use to sing, suggesting a common evolutionary origin for the complex behaviors.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFossil finds put gibbons in Asia as early as 8 million years ago
Specimens from China raise questions about the evolutionary ID of an even older ape tooth from India.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsVideo shows the first red fox known to fish for food
Big fish in shallow water are easy pickings for one fox — the first of its kind known to fish, a study finds.
By Freda Kreier -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsThis environmentally friendly quantum sensor runs on sunlight
Quantum sensors often rely on power-hungry lasers to make measurements. A new quantum magnetometer uses sunlight to measure magnetic fields instead.
-
 Life
LifeHere’s what triggers giant honeybees to do the wave
A new study is revealing details about what sets off a defensive behavior in open-nesting bees known as shimmering.
By Ananya -
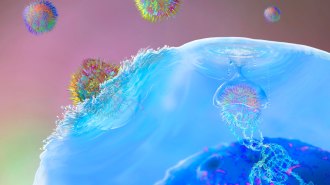 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine5 people with lupus are in remission after CAR-T cell treatment
More than six months after CAR-T cell treatment, five patients are in remission and have functional immune systems.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSaturn’s rings and tilt might have come from one missing moon
The hypothetical moon, dubbed Chrysalis, could have helped tip the planet over before getting shredded to form the rings, researchers suggest.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyLooking for a job? Lean more on weak ties than strong relationships
A 50-year-old social science theory gets put to the test in a new study using data on 20 million LinkedIn users.
By Sujata Gupta -
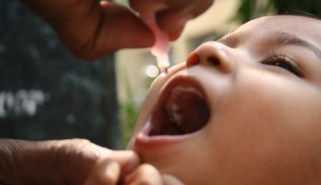 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePoliovirus is spreading in New York. Here’s what you need to know
With signs of poliovirus spreading in a handful of counties in New York, unvaccinated people could be at risk of paralytic polio.
-
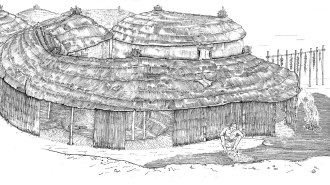 Anthropology
AnthropologyHumans may have started tending animals almost 13,000 years ago
Remnants from an ancient fire pit in Syria suggest that hunter-gatherers were burning dung as fuel by the end of the Old Stone Age.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFalling objects in orbit show Einstein was right — again
For more than two years, a pair of metal cylinders fell at the same rate in space, confirming the equivalence principle, a key tenet of general relativity.