News
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryElusive acid finally created
Cyanoform, a chemical sought for more than a century and written into textbooks, is one of the strongest organic acids.
By Beth Mole -
 Astronomy
AstronomyBlack hole collisions evade detection
The environment in the centers of some galaxies might inhibit gravitational waves radiating from supermassive black holes, a new study suggests.
-
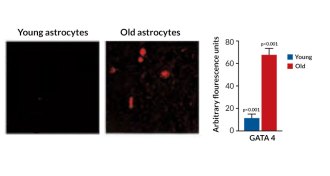 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat makes cells stop dividing and growing
Scientists have found that the protein GATA4 helps control cellular senescence, and may be a target for treating aging-related diseases.
-
 Life
LifeFor people, mealtime is all the time
People eat for most of their waking hours, which may affect sleep and weight.
-
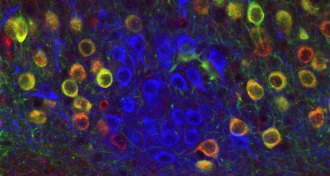 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSeparate cell types encode memory’s time, place
Cells called ocean cells help store a memory’s “where,” while other cells called island cells help store a memory’s “when.”
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum choice can be counterproductive
In a puzzling paradox, delivering quantum messages becomes more difficult if the intended recipient offers the sender multiple options for the time and place of delivery.
By Andrew Grant -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyHanded-down tales tell of ancient sea level rise
Australian Aborigines tell tales of actual, ancient sea-level rises, a contested study finds.
By Bruce Bower -
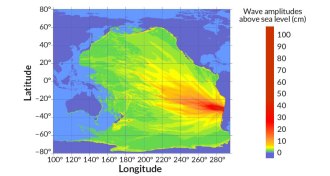 Earth
EarthShortcut math predicts tsunami height quickly
The September 16 earthquake that rattled Chile proved an unexpected test for new numerical calculations that could provide quicker forecasts of incoming tsunamis.
-
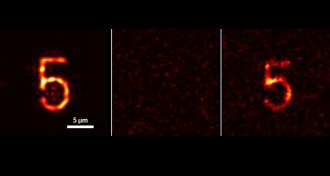 Physics
PhysicsRaw chicken, ingenuity make a time-reversal mirror
A new phase-conjugation mirror sends light waves back where they came from, allowing physicists to reconstruct images even if the original light was severely scrambled.
By Andrew Grant -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy finds benefits from lowering blood pressure, but questions remain
Preliminary results from NIH clinical trial suggest that lower blood pressure is better, but scientists have not yet published the data and open questions remain.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeOld stem cell barriers fade away
Barrier that keeps aging factors out of stem cells breaks down with age.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyRocky families, not same-sex parents, blamed for kids’ troubles in adulthood
Range of adult problems linked to childhood family changes, not gay parents.
By Bruce Bower