News
-
 Oceans
OceansOxygen in Black Sea has declined by more than a third since 1955
The Black Sea’s oxygen-rich surface layer shrank by more than a third from 1955 through 2013, compressing marine habitats and bringing toxic hydrogen sulfide closer to the surface.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsChemical tags on DNA appear to differ between gay and straight men
DNA marks distinguished homosexual men from heterosexual men with in a small twin study.
-
 Humans
HumansInto Africa: Ancient skeleton sheds light on reverse migration
Ancient man’s DNA helps reveal extent of Eurasian farmers’ back-to-Africa migration some 3,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyNobels note neutrinos, DNA, drugs
The Nobel Prizes in physics, chemistry and physiology or medicine ran the gamut this year, honoring both fundamental science discoveries and research with real-world impacts.
-
 Chemistry
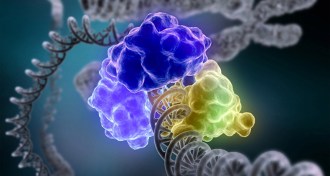
ChemistryChemistry Nobel granted for deciphering DNA repair
Three researchers win chemistry Nobel for working out how cells fix damaged genetic material
By Meghan Rosen and Sarah Schwartz -
 Animals
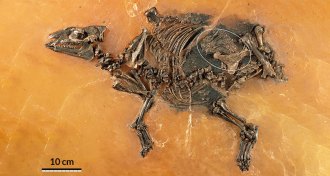
AnimalsOldest pregnant horselike fossil found
A 48-million-year-old fossil of an early horse and fetus is the oldest and best-preserved specimen of its kind.
-
 Animals
AnimalsNo eyes, no problem for color-sensing coral larvae
Switching colors of underwater light can switch preferences for where staghorn corals choose their forever homes.
By Susan Milius -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNeutrinos’ identity shift snares physics Nobel
Arthur McDonald and Takaaki Kajita shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery that neutrinos oscillate between different types, which demonstrates that the particles have mass.
By Andrew Grant and Thomas Sumner -
 Humans
HumansChimpanzees show surprising flexibility on two feet
Chimpanzees’ upper-body flexibility while walking upright suggests ancient hominids walked effectively.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNobel medicine prize won for drugs from natural sources
Nobel Prizes in medicine or physiology awarded for drugs that combat roundworms and malaria
By Tina Hesman Saey and Laura Sanders -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFull coverage: 2015 Nobel Prizes
The Nobel Prizes in physics, chemistry and medicine or physiology ran the gamut this year, honoring both fundamental science discoveries and research with real-world impacts.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFizzy bubbles carry drugs deep into wounds
Bubble-powered drugs burrow into wounds to stop blood loss.
By Meghan Rosen