News
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsLight mimics hotel with limitless vacancies
By mimicking a mathematician’s method for creating vacancies in a hotel with an infinite number of rooms, physicists may have found a way of increasing the amount of data that can be carried via light.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsSalamander ancestors could regenerate limbs
Salamanders and ancient amphibians share similar way of regenerating limbs.
-
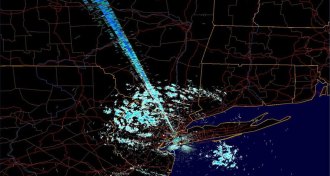 Climate
ClimateWi-Fi threatens weather forecasts
Interference from wireless technology threatens the usefulness of weather radar, meteorologists warn.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSigns of Alzheimer’s seen in young brain’s GPS cells
Signs of Alzheimer’s can show up in the brain’s compass decades before symptoms strike.
By Meghan Rosen -
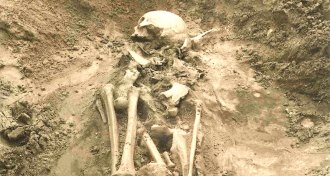 Anthropology
AnthropologyPlagues plagued the Bronze Age
Ancient bacterial DNA provides first clues to Bronze Age plagues in Europe and Asia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsHow architecture can make ants better workers
The right nest architecture can make harvester ants better at their job, new research shows.
By Susan Milius -
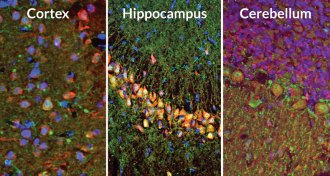 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNets full of holes catch long-term memories
Tough structures that swaddle nerve cells may store long-term memories.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDNA trail leads to new spot for dog domestication
A new study suggests that dogs were first domesticated in Central Asia.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSigns of Huntington’s show up in the brain in childhood
Hints of Huntington’s disease show up in the brain long before symptoms do.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew evidence weakens case against climate in woolly mammoths’ death
Hunters responsible for woolly mammoths’ extinction, suggests a chemical analysis of juveniles’ tusks.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDimetrodon’s diet redetermined
The reptilelike Dimetrodon dined mainly on amphibians and sharks, not big herbivores as scientists once believed.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
AnthropologySleep time in hunter-gatherer groups on low end of scale
Hunter-gatherer communities in Africa and South America have similar sleeping patterns as people living in postindustrial societies, researchers find.