News
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyEnormous black hole resides at core of tiny galaxy
A small galaxy stores 15 percent of its mass in a black hole, suggesting compact galaxies might be shreds of once larger galaxies.
-
 Earth
EarthShrinking ancient sea may have spawned Sahara Desert
The Saharan Desert probably formed 7 million years ago as the ancient Tethys Sea, the forerunner of the Mediterranean Sea, shrank.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceMaking metamaterials ‘digital’ could simplify invisibility cloaks
The digital world of 1s and 0s has inspired a simpler way to make complex metamaterials.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeArtificial sweeteners may tip scales toward metabolic problems
The artificial sweetener saccharin meddles with the gut’s microbial community, setting in motion metabolic changes associated with obesity and diabetes.
-
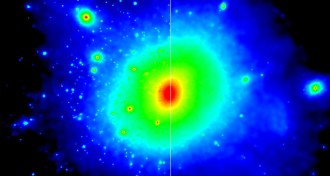 Astronomy
AstronomyTweak to dark matter may explain Milky Way mystery
Dark matter weakly interacting with light in the early universe might have prevented satellite galaxies from forming around Milky Way, astronomers propose.
-
 Tech
TechHydrogen made using sunlight, cheap materials
Photosynthesis-inspired fuel cell uses water to make hydrogen gas and could feature in next-generation cars.
By Sam Lemonick -
 Agriculture
AgricultureDrug-resistant staph can cling to farm workers for days
Agricultural exposure to staph bacteria could threaten the health of laborers and people who live near farms, a study of pig farm workers suggests.
By Beth Mole -
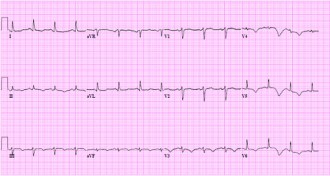 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMass EKG screening for athletes inadvisable, panel says
Only athletes with warning signs of cardiac problems should be tested with electrocardiograms, according to the American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology.
By Laura Beil -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsEvidence for new Higgs-related particle fades away
A close look at data from the Large Hadron Collider finds no evidence that the Higgs boson decays into a new, unknown particle.
By Andrew Grant -
 Life
LifeVagina bacteria make molecules that could be drugs
Microbes on the human body are capable of producing thousands of small molecules that hold potential as drugs.
-
 Earth
EarthWarming alone triggered Antarctic ice shelf collapse
Warming surface temperatures, not an unstable foundation, probably doomed Antarctica’s Larsen B ice shelf.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental herpes drug outperforms first-line med
An experimental treatment for genital herpes suppresses the viral infection better than the standard drug, but animal tests raise concerns about side effects.
By Nathan Seppa