News
-
 Planetary Science
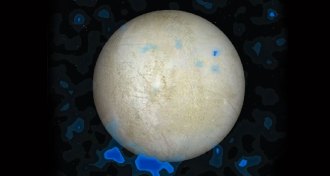
Planetary ScienceEuropa vents water, Hubble data suggest
Plumes from ice-covered oceans would increase likelihood of life-friendly conditions on one moon of Jupiter.
By Andrew Grant -
 Climate
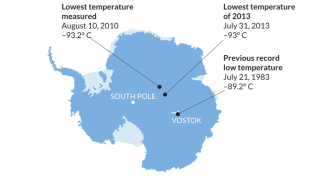
ClimateColdest place moves from one Antarctic site to another
New record low measured by satellite.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsLizard breath has surprising birdlike flow
Decades of assumptions may be wrong about the evolution of reptile lungs.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeDietary changes affect gut microbes within a day
Menu restricted to meat, egg and cheese alters bacterial mix more than eating only plants.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeartburn drugs linked to vitamin deficiency
People who take Nexium, Prilosec and other medicines more prone to low B12 levels.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain chip enables injured rats to control movements
Prosthesis bypasses damaged area to connect distant neurons.
-
 Math
MathTwin primes and prime bunches in mathematicians’ crosshairs
For second time this year, a mathematician makes a major advance toward proving a long-standing conjecture.
-
 Neuroscience
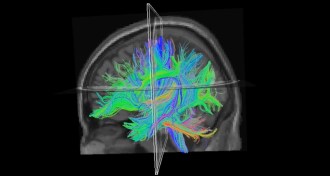
NeuroscienceFaulty brain wiring may contribute to dyslexia
Adults with the disorder showed difficulty transmitting information among areas that process language.
By Beth Mole -
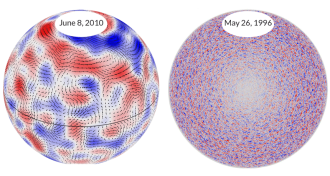 Astronomy
AstronomySun’s rotation driven by enormous plasma flows
Long-lasting plasma flows 15 times the diameter of Earth transport heat from the sun’s depths to its surface, helping explain solar rotation.
-
 Life
LifeAutism may have link to chemicals made by gut microbes
Beneficial bacteria improved abnormal behaviors in mice with altered intestines.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient hominid bone serves up DNA stunner
Spanish hominid fossil from 400,000 years ago reveals genetic ties to Asia’s mysterious Denisovans.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyISON appears to have broken up after brush with sun
Comet ISON has disintegrated in the sun’s intense heat and gravity, according to a growing consensus among astronomers.