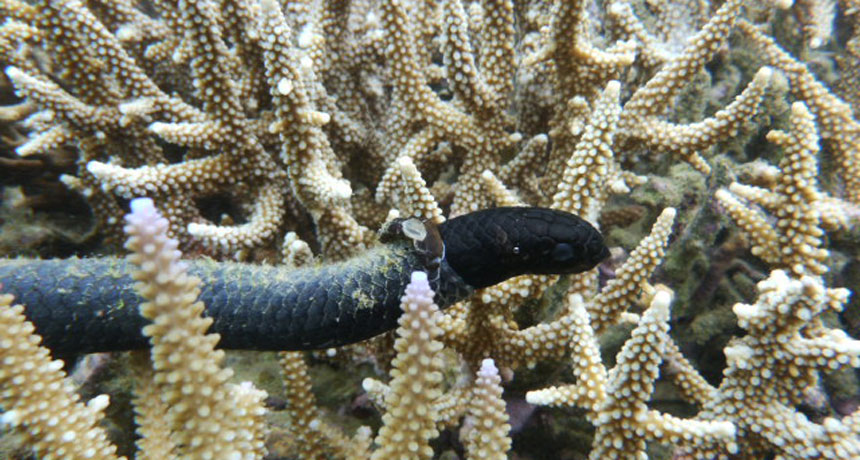
DARK MARK This dark form of a turtle-headed sea snake is shedding its skin, and maybe some toxic trace metals along with it.
C. Goiran
Maybe it’s more than reptile fashion. The high percentage of citified sea snakes wearing black might be a sign that pollution is an evolutionary force.
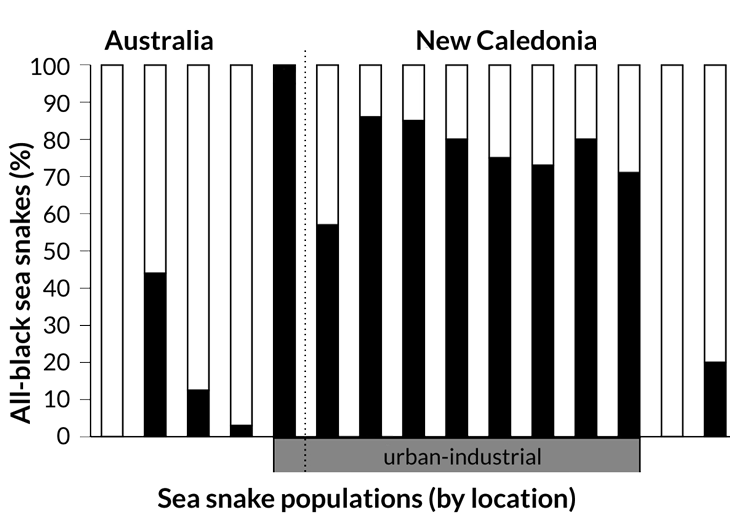
Off the coasts of Australia and New Caledonia, some turtle-headed sea snakes (Emydocephalus annulatus) sport pale bands on their dark skins. Others go all black. In 15 places surveyed, the all-black form was more likely to predominate in waters near cities, military sites or industrial zones than along reefs near less built-up coastlines, says evolutionary ecologist Rick Shine of the University of Sydney.
That trend plus some analysis of trace elements in snakes’ skin suggests that the abundant dark forms could turn out to be an example of industrial melanism, Shine and his colleagues propose August 10 in Current Biology.
The most famous example of this evolutionary phenomenon comes from a dark form of peppered moth that overtook pale populations in 19th century England (SN: 6/25/16, p. 6). Dark wings created better camouflage from hungry birds in the grimy industrializing landscape.

This could explain why marine biologist and study coauthor Claire Goiran has so many dark turtle-headed sea snakes in a lagoon not far from her campus, the University of New Caledonia in Nouméa. Earlier studies had found only downsides to dark coloration: Seaweed spores preferentially settle on dark snakes and sprout fuzz that can cut swimming speed by 20 percent and cause a snake to shed its skin more often than normal.
To test a scenario of industrial melanism, or darkening due to pollution, the researchers collected data on skin colors for a total of about 1,450 snakes, both live and museum specimens, from 15 sites in New Caledonia and Australia. Higher percentages of all-dark snakes wriggled around the nine polluted sites surveyed. At one, a remote Australian reef that the military had long used as a bombing range, all 13 specimens were dark.
To test shed skins for trace metals, Goiran and Shine enlisted Paco Bustamante of the University of La Rochelle in France, who studies trace metal contamination in marine life.
Researchers managed to collect sloughed skins from 17 turtle-headed snakes, which inconveniently shed their skin underwater. To compare light and dark patches, the scientists turned to two local species of sea kraits, which have banded skin and visit land to shed it.
Story continues after graph
Where dark snakes abound
At 15 sites in Australia and New Caledonia, either museum collections or surveys of live snakes showed the percentage of turtle-headed sea snakes with dark coloring. Of 1,456 snakes examined, 1,153 came from three of the New Caledonia industrial sites.
Overall, skins held concentrations of trace elements higher than those that can cause health problems in birds and mammals, the researchers report. In the krait skins, dark zones had slightly more of some contaminants, such as zinc and arsenic, than the pale bluish-white bands did.
The idea that polluted water favors melanized sea snakes “is a reasonable hypothesis based on what we know,” Chatelain says. Definitive tests will require more data and different approaches. Genetic testing, for example, would clarify whether dark populations arose instead from small groups of pioneers that happened to have a lot of black snakes.
That testing could be a long way off. Sea snakes are evolutionary cousins of cobras and mambas, and some of the species swimming around Australia and New Caledonia are “bowel-looseningly large,” Shine says. At least the little turtle-headed ones, which eat eggs of small reef fishes, have venom glands that have atrophied and “probably couldn’t fit a human finger in their mouths.” But until someone figures out how to keep them alive in captivity for more than a few days, Shine isn’t expecting definitive genetics.