
Laura Sanders reports on neuroscience for Science News. She wrote Growth Curve, a blog about the science of raising kids, from 2013 to 2019 and continues to write about child development and parenting from time to time. She earned her Ph.D. in molecular biology from the University of Southern California in Los Angeles, where she studied the nerve cells that compel a fruit fly to perform a dazzling mating dance. Convinced that she was missing some exciting science somewhere, Laura turned her eye toward writing about brains in all shapes and forms. She holds undergraduate degrees in creative writing and biology from Vanderbilt University in Nashville, where she was a National Merit Scholar. Growth Curve, her 2012 series on consciousness and her 2013 article on the dearth of psychiatric drugs have received awards recognizing editorial excellence.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
All Stories by Laura Sanders
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceWiggling ears may have once helped us hear
These ancient ear muscles may provide a readout of a person's hearing efforts.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA man volunteered to get brain implants for depression. Hear his story
In the first episode of The Deep End Podcast, we meet Jon Nelson, who shares why he volunteered to get brain implants for his relentless depression.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSleeping pills may have unexpected effects on the snoozing brain
As scientists unravel how sleep benefits the body, a study in mice is highlighting the potential pitfalls of using Ambien and other sleep aids.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePlastic shards permeate human brains
A study of microplastics and nanoplastics in brains shows an astonishing increase over time.
-
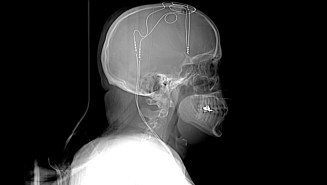 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWelcome to The Deep End, a new podcast about brain implants and depression
This new six-part podcast follows the lives of people with severe depression who volunteered for deep brain stimulation.
-
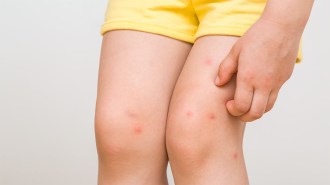 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceScratching an itch is so good, and so bad
The motion kicks off inflammation but may also combat harmful bacteria
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGot a cold? A placebo might help
Amid doubts over a common decongestant, evidence suggests the placebo effect can still help people suffering from a cold.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow people suppress memories may be key to PTSD recovery
People who recovered from PTSD changed the way their brains handle intrusive thoughts, a study of survivors of the 2015 Paris terrorist attacks shows.
-
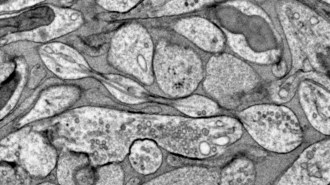 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe message-sending part of neurons may be blobby, not smooth
Axons can be shaped like strings of pearls, research in mice and people show. How that shape may influence brain signaling is not yet clear.
-
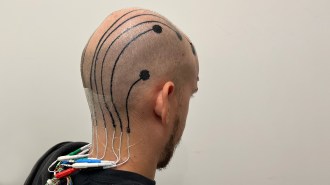 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElectronic ‘tattoos’ offer an alternative to electrodes for brain monitoring
A standard EEG test requires electrodes that come with pitfalls. A spray-on ink, capable of carrying electrical signals, avoids some of those.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVaccines, fluoride, raw milk: How RFK Jr.’s views may shape public health
If confirmed as head of the Department of Health and Human Services, Kennedy could influence U.S. policy on vaccines, drugs and food safety.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSome people don’t have a mind’s eye. Scientists want to know why
The senses of sight and sound are usually mingled in the brain, but not for people with aphantasia.