Genetics
-
 Animals
AnimalsIn a first, genetically modified silkworms produced pure spider silk
An effort to engineer silkworms to produce spider silk brings us closer than ever to exploiting the extraordinary properties of this arachnid fiber.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGene editing can make chickens resistant to bird flu
Chickens genetically modified to be impervious to avian influenza may one day prevent the spread of the disease on farms, a study suggests.
-
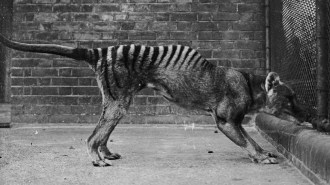 Animals
AnimalsFor the first time, researchers decoded the RNA of an extinct animal
The Tasmanian tiger, or thylacine, was hunted nearly to extinction. Now RNA extracted from a museum specimen reveals how its cells functioned.
-
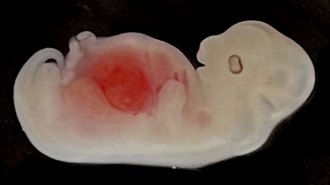 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists grow humanized kidneys in pig embryos
The work represents an important advance in the methods needed to grow humanized kidneys, hearts, and pancreases in animals.
By Amanda Heidt -
 Animals
AnimalsA new DNA leaf swab technique could revolutionize how we monitor biodiversity
Simple swabs of just 24 leaves in Uganda’s Kibale National Park provided a genetic snapshot of 52 animals in the tropical forest.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe Y chromosome’s genetic puzzle is finally complete
New analyses of the human Y chromosome reveal millions of new bases and different locations for the same gene in different people.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsA new look at Ötzi the Iceman’s DNA reveals new ancestry and other surprises
Ötzi had genetic variants for male-pattern baldness and dark skin, and he also had an unusual amount of early farmer ancestry, a new DNA analysis finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsThe ‘unknome’ catalogs nearly 2 million proteins. Many are mysterious
Scientists have unveiled a new database that emphasizes how much we still don’t know about human proteins and genes.
By Skyler Ware -
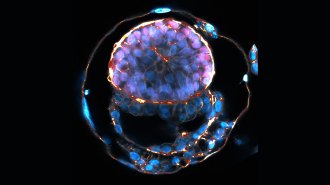 Humans
HumansHuman embryo replicas have gotten more complex. Here’s what you need to know
Lab-engineered human embryo models created from stem cells provide a look at development beyond the first week. But they raise ethical questions.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyHow Asia’s first nomadic empire broke the rules of imperial expansion
New studies reveal clues to how mobile rulers assembled a multiethnic empire of herders known as the Xiongnu more than 2,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Genetics
GeneticsThe first gene therapy for muscular dystrophy has been approved for some kids
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration cleared a shortened version of a gene for a muscle protein to be used in 4- and 5-year-olds with muscular dystrophy.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDaphne Martschenko is a champion for ethical, inclusive genomics research
A bioethicist focused on the genomics revolution, Daphne Martschenko fosters open discussion through “adversarial collaboration”