Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineElephants’ cancer-protection secret may be in the genes
An extra dose of cancer-fighting genes may be the secret to elephants’ long life spans.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhy kids look funny when they run
Kids’ short legs give them little time to push high off the ground, a constraint that leads to the jerky toddler trot.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWeight and sun exposure linked to onset of multiple sclerosis
Among people with multiple sclerosis, those with higher body mass and lower adolescent sun exposure tended to be diagnosed with the disease at an earlier age, a new study suggests.
-
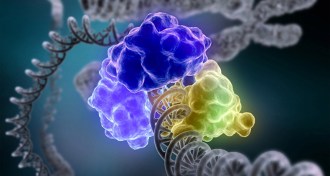 Genetics
GeneticsChemistry Nobel honors studies of DNA repair mechanisms
Studies of DNA’s repair mechanisms have won Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar the 2015 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Sarah Schwartz and Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNobel medicine prize won for drugs from natural sources
Nobel Prizes in medicine or physiology awarded for drugs that combat roundworms and malaria
By Tina Hesman Saey and Laura Sanders -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTherapies against roundworm, malaria parasites win medicine Nobel
The 2015 Nobel Prize in medicine or physiology was awarded to Youyou Tu for her work in counteracting malaria, and to William Campbell and Satoshi Omura for work on treatments against roundworm parasites.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFizzy bubbles carry drugs deep into wounds
Bubble-powered drugs burrow into wounds to stop blood loss.
By Meghan Rosen -
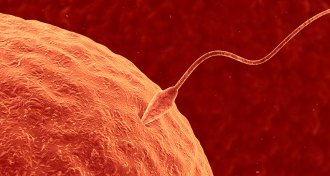 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSperm protein may offer target for male contraceptive
With the identification of a new sperm protein that helps sperm penetrate eggs, researchers may be closer to developing birth control pills for men.
By Meghan Rosen -
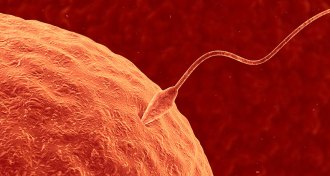 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSperm protein may offer target for male contraceptive
With the identification of a new sperm protein that helps sperm penetrate eggs, researchers may be closer to developing birth control pills for men.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeBabies low on key gut bacteria at higher risk of asthma
Asthma risk may be set early in life, but mice data suggest that the risk could altered by friendly gut bacteria.
-
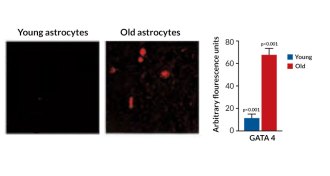 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat makes cells stop dividing and growing
Scientists have found that the protein GATA4 helps control cellular senescence, and may be a target for treating aging-related diseases.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving sex doesn’t trigger heart attacks, study suggests
Sex doesn’t trigger heart attacks, study of patients with cardiovascular disease suggests.
By Meghan Rosen