Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLethal snake venom may be countered by new AI-designed proteins
The current way to produce antivenoms is antiquated. Experiments in mice suggest that an artificial intelligence approach could save time and money.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsIron Age Celtic women’s social and political power just got a boost
Ancient DNA indicates women stayed in their home communities and married partners from outside the area.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineObesity needs a new definition beyond BMI, health experts argue
Experts say clinical obesity is more than a high BMI and instead is a disease in which excess body fat harms tissues, organs or doing daily activities.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGot a cold? A placebo might help
Amid doubts over a common decongestant, evidence suggests the placebo effect can still help people suffering from a cold.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineU.S. dementia cases may rise to 1 million per year by 2060
Baby Boomers may drive a drastic increase in dementia cases in coming decades, but there are steps people can take to reduce their risk.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAI could transform health care, but will it live up to the hype?
AI has the potential to make health care more effective, equitable and humane. Whether the tech delivers on these promises remains to be seen.
By Meghan Rosen and Tina Hesman Saey -
 Humans
HumansHow child soldiers heal after the trauma of war
For more than two decades, Theresa Betancourt has studied Sierra Leone’s former child soldiers. Her new book Shadows into Light tells their stories.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIs alcohol linked to cancer? Here’s what the science says
A new U.S. Surgeon General's report describes the link between drinking alcohol and developing cancer. Many Americans aren’t aware of the risk.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat to know about the first bird flu–related death in the U.S.
H5N1 has infected 66 people in the United States since early 2024, mostly causing mild illness. A Louisiana man was the first to get severely sick.
-
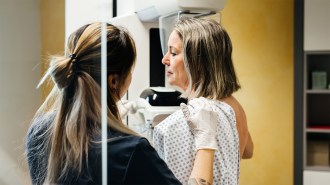 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineAI helps doctors detect more breast cancer in the largest real-world study
AI is as good as clinicians at interpreting mammograms, a cancer study with nearly 500,000 participants in Germany suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe spread of breast cancer may be inherited
A variant of PCSK9, a gene involved in raising cholesterol, may spur metastasis. An approved antibody might stop it.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineShort bursts of physical activity cut women’s risk of heart attack
Even just a few minutes of vigorous movement per day lowers the risk of serious cardiovascular problems, like heart attack and heart failure, in women.
By Meghan Rosen