
Neuroscience
Why is math harder for some kids? Brain scans offer clues
Kids with math learning disabilities process number symbols differently than quantities shown as dots — and it shows up in MRIs.
By Lily Burton
Every print subscription comes with full digital access

Kids with math learning disabilities process number symbols differently than quantities shown as dots — and it shows up in MRIs.
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.

Fecal analyses and necropsies suggest a fire-footed rope squirrel was the source of a 2023 mpox outbreak among sooty mangabeys in Côte d’Ivoire.

During a test drive, the mobile lab van uncovered a drug-resistant HIV strain that sprung up after the ongoing war with Russia started.

A land dispute may have led to the massacre 3,000 years ago, suggesting Europe’s transition to farming wasn’t always peaceful.

A new study suggests that inherited traits explain a small but measurable share of why some people relocate far from where they were born.

The TRPV4 protein’s dual nature, found in studies with mice, may complicate the hunt for human itch treatments
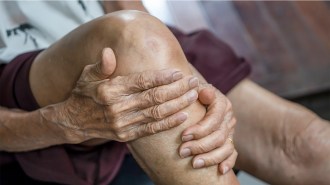
A study in mice and people with osteoarthritis suggests semaglutide can bulk up cartilage between bones, though bigger trials are needed to confirm.

We can take some clues from hibernation and cryogenics, but humans aren't yet built for that kind of deep sleep.

The framework predicts how proteins will function with several interacting mutations and finds combinations that work well together.

Breast exams, birth control and family planning are just some of the reasons not to skip your annual ob-gyn appointment.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber?
Become one now.