Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
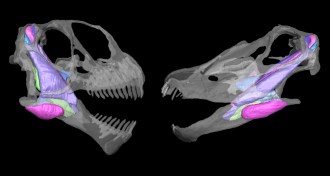 Paleontology
PaleontologyPlant-eating dinosaurs coexisted by munching different vegetation
Differences in skulls allowed sauropods to coexist in an arid landscape by enabling the dinosaurs to tackle different plants.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMelatonin and the watery beginnings of sleep
The tiny zooplankton Platynereis dumerilii use melatonin just as much as we do, suggesting that the origins of sleeplike behavior may lie under the sea.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNeuroscientists garner Nobel for discovering brain’s ‘inner GPS’
Three researchers who found brain cells that allow rats to orient themselves in space have won the 2014 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine.
-
 Animals
Animals‘Planet of the Bugs’ reveals the secrets to insects’ success
Entomologist Scott Richard Shaw explores the evolution of insects and how they came to rule the world.
By Sid Perkins -
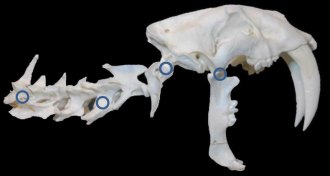 Animals
AnimalsHow a saber-toothed cat is like a can opener
A researcher argues that the saber-toothed cat’s teeth acted like an old-fashioned can opener.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s map cells win three scientists Nobel Prize
The discovery of brain cells that provide a sort of “inner GPS” has been awarded the 2014 Nobel Prize for physiology or medicine.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHelp scientists find floating forests of kelp
By looking for signs of kelp in satellite images, citizen scientists can help researchers keep track of the world’s seaweed forests.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHuman ingenuity takes on Mother Nature in ‘The Big Ratchet’
Geographer Ruth DeFries explains how technological innovations have allowed humans to overcome environmental challenges throughout history.
-

-
 Plants
PlantsClimbing high to save a threatened West Coast plant
A group of scientists hopes to save a cliff-hugging plant threatened by invasive grasses, drought and fire in California’s Santa Monica Mountains.
By Nsikan Akpan -
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive rabbitfish team up to raze algal forests
Tropical rabbitfish have expanded into temperate Mediterranean waters, where they destroy algae forests by gobbling both young and adult algae.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLacking ice, huge walrus herd congregates on Alaska shore
A large group of walruses has hauled out on the beach near Point Lay, Alaska. The animals have been forced onto shore due to a lack of sea ice in the region.