Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsThe unsung women of quantum physics get their due
The new book, Women in the History of Quantum Physics, spotlights the oft-forgotten contributions of women scientists in the field.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsAs quantum mechanics turns 100, a new revolution is under way
With greater control over the quantum realm, physicists are poised to make major leaps in quantum computing, quantum gravity and more.
-
 Tech
TechNew audio tech could let you listen privately without headphones
Private listening out in the open is possible thanks to acoustic metasurfaces that precisely bend and direct sound waves.
-
 Plants
PlantsA leaf’s geometry determines whether it falls far from its tree
Shape and symmetry help determine where a leaf lands — and if the tree it came from can recoup the leaf’s carbon as it decomposes.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLining medical stents with hairlike fuzz could fend off infections
Implanted tubes that transport bodily fluids can get gross. A lab prototype suggests a new vibration-based way to keep them clean and prevent infection.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists explain how cheese rosettes form
Rosettes made by scraping Tête de Moine, or “monk’s head,” cheese result from variations in the friction between the blade and the cheese.
-
 Physics
PhysicsHere’s how we might generate electricity from rain
Water drops produce electricity when dripped through a small tube. That power might be harnessed as renewable energy in rainy places.
By Jude Coleman -
 Physics
PhysicsImitation dark matter axions have arrived. They could reveal the real thing
A long-elusive, hypothetical subatomic particle called the axion can be simulated and potentially detected in a type of thin material.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNeutrinos’ maximum possible mass shrinks further
The KATRIN experiment in Germany nearly halved the maximum possible mass for neutrinos, setting it at 0.45 electron volts.
-
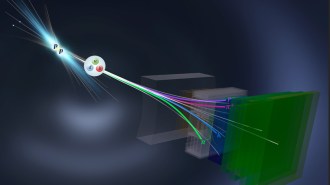 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsPhysicists have confirmed a new mismatch between matter and antimatter
Charge-parity violation is thought to explain why there’s more matter than antimatter in the universe. Scientists just spotted it in a new place.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsPhysicists are mostly unconvinced by Microsoft’s new topological quantum chip
Majorana qubits could be error resistant. But after a contentious talk at the Global Physics Summit, scientists aren’t convinced Microsoft has them.
-
 Physics
PhysicsCalls to restart nuclear weapons tests stir dismay and debate among scientists
Many scientists say “subcritical” experiments and computer simulations make nuclear weapons testing unnecessary.