All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGaming-type setup relieves phantom limb pain
The treatment reduced one patient’s pain entirely for periods of time and helped him sleep without being awoken by pain.
-
 Agriculture
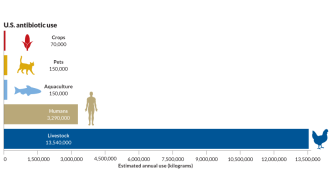
AgricultureWhere antibiotics go
Of the 51 tons of antibiotics consumed every day in the United States, about 80 percent goes into animal production.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAlgal blooms created ancient whale graveyard
Whales and other marine mammals died at sea and were buried on a tidal flat in what's now in the Atacama Desert in Chile.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBereavement can take toll on health, not just emotions
In the month after a partner dies, spouse more prone to heart attack, stroke.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Psychology
PsychologySuicide rates drop in big cities
With more social connections, people may be less inclined to take their own lives.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
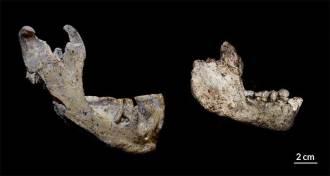
AnthropologyHuman ancestors at West Asian site deemed two species
Researchers see two species instead of one at oldest known Homo site outside Africa.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyStar cluster hurtles through space with tremendous speed
A compact ball of hundreds of thousands of stars has just shot out of the galaxy M87 at millions of kilometers per hour, astronomers report. It is the first hypervelocity globular cluster detected to date.
-
 Astronomy
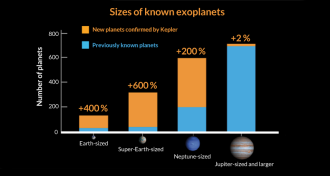
AstronomyKepler space telescope data uncovers 715 new planets
Astronomers used a new tool to quickly confirm the detection of exoplanets.
-
 Physics
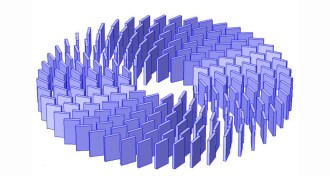
PhysicsMetamaterials give sound a twist
The design allows researchers rotate a wave at precise angles so that it originates from the opposite direction, which could have implications for improving ultrasound imaging.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental drug no Methuselah formula
Compound lets mice live healthier lives but doesn't extend life span.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGirls may require more mutations than boys to develop autism
New results may help explain why more males wind up with autism.
-
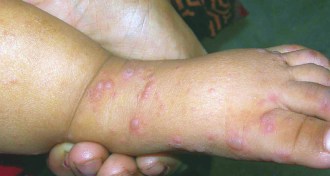 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental vaccines protect children from hand, foot and mouth disease
Shots prevented cases resulting from enterovirus 71.
By Nathan Seppa