All Stories
-
 Life
LifeEncountering an unexpected Pluto and life’s complexity
Just as genetic analyses are revealing details of life’s long history, the New Horizons probe is bringing the fuzzy surface of Pluto into focus.
By Eva Emerson -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceGlobal warming unpaused, how space affects the brain and more reader feedback
A reader shares a story about Stephen Jay Gould, while others discuss how to protect the brain from radiation in space and whether 2014 was the hottest year on record.
-
 Life
LifeThe tree of life gets a makeover
Biology’s tree of life has morphed from the familiar classroom version emphasizing kingdoms into a complex depiction of supergroups, in which animals are aligned with a slew of single-celled cousins.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow trans fats oozed into our diet and out again
Trans fats are no longer “generally recognized as safe” by the FDA. In a world where we want to have our doughnuts and eat them, too, it’s back to the drawing board, and back to butter.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineResveratrol’s anticancer benefits show up in low doses
Small amounts of the compound found in red wine and grapes prove protective against colon cancer in mice fed a high-fat diet.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyDistant star has northern lights–like display
A dim star shows signs of auroral lights, the first detected on a body that’s not a planet or moon.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyRemains of Jamestown leaders discovered
Colonial-era graves reveal leading figures in founding of English America.
By Bruce Bower -
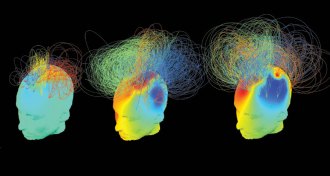 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain activity in unconscious patients offers new views of awareness
As more people survive serious brain injury, researchers are using EEG and fMRI to learn who is aware inside an unresponsive body.
By Laura Beil -
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsEncased algae create kaleidoscope of color
The skeletons of diatoms, algae that produce oxygen but also form toxic blooms, can create beautiful microscopic designs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOn the importance of elephant poop
Asian elephants are key dispersers for tree seeds. A new study finds that buffalo and cattle can also disperse the seeds, but not nearly as well.
-
 Animals
AnimalsToddler seahorses are bumbling and adorable
Rice-grain-sized youngsters can’t yet get a grasp with their tails.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceAge affects brain’s response to anesthesia
Anesthesia has different effects on young and old brains.