News
-
 Psychology
PsychologyAfrican farmers’ kids conquer the marshmallow test
Nso farmers in Cameroon groom kids for self-control that Western peers often lack.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyEclipse watchers catch part of the sun’s surface fleeing to space
A serendipitous eruption during a solar eclipse showed relatively cool blobs of plasma, wrapped in a million-degree flame, streaming from the sun.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyAncient attack marks show ocean predators got scarier
Killer snails and other ocean predators that drill through shells have grown bigger over evolutionary time.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthMagma stored under volcanoes is mostly solid
Ancient zircon crystals provide clues about the magma that fuels volcanic eruptions.
-
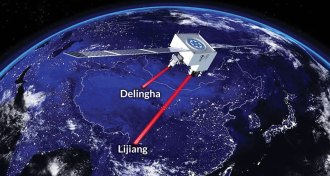 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum satellite shatters entanglement record
A satellite sent entangled particles to two Chinese cities 1,200 kilometers apart.
-
 Life
LifeHow bearded dragons switch their sex
RNA editing might affect reptile sex determination at temperature extremes.
-
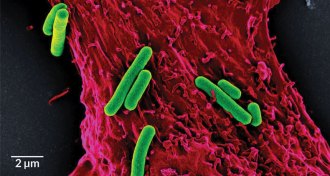 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew heart attack treatment uses photosynthetic bacteria to make oxygen
Photosynthetic bacteria can produce oxygen to keep rat heart muscles healthy after a heart attack.
-
 Life
LifeAncient DNA shakes up the elephant family tree
DNA from straight-tusked elephant fossils is forcing scientists to reconsider the history of elephant evolution.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineNew kind of ‘tan in a bottle’ may one day protect against skin cancer
A drug for activating melanin production without using ultraviolet radiation works in human skin samples.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceJupiter’s precocious birth happened in the solar system’s first million years
Jupiter formed within the first million years of the solar system, according to meteorite measurements.
-
 Physics
PhysicsWater circling a drain provides insight into black holes
Water waves scattering off a vortex can exhibit rotational superradiance, an effect predicted to appear in black holes.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFaux particles commit physics faux pas
Quasiparticles present in a solid material break the rules of particle physics.