News
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain activity helps build an alpha male
In mice, nerve cells in the prefrontal cortex influence whether an individual is dominant or submissive.
-
 Earth
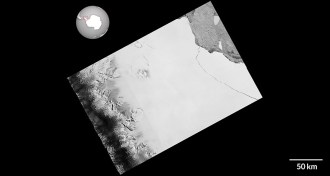
EarthDelaware-sized iceberg breaks off Antarctic ice shelf
An iceberg about the size of Delaware splintered from the Larsen C ice shelf in one of the largest calving events ever recorded.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe fight against gonorrhea gets a potential new weapon: a vaccine
A vaccine used in New Zealand to curb meningitis also appeared to drop gonorrhea infections, results that hint at a way to make a gonorrhea vaccine.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceJust one night of poor sleep can boost Alzheimer’s proteins
Deep sleep may prevent the buildup of Alzheimer’s proteins.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineDrinking sugary beverages in pregnancy linked to kids’ later weight gain
Consuming sugary drinks while pregnant may mean kids are heavier when they reach elementary school age.
-
 Plants
PlantsHermaphrodite wildflower has its own battle of the sexes
A new example of sexual conflict shows up in a plant with a troublesome pollinator.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsHow to eavesdrop on kelp
Sounds reverberating through a kelp bed can be linked to environmental factors, suggesting a low-key way to monitor undersea communities.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDouble-duty DNA plays a role in birth and death
Coronary artery disease may be the price humans pay for improved fertility.
-
 Planetary Science
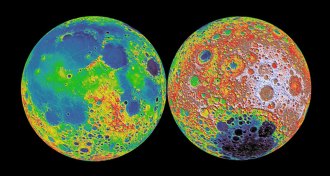
Planetary ScienceThe moon might have had a heavy metal atmosphere with supersonic winds
Heat from a glowing infant Earth could have vaporized the moon’s metals into an atmosphere as thick as Mars’, a new simulation shows.
-
 Plants
PlantsPetunias spread their scent using pushy proteins
Scent molecules hitch a ride on a particular protein to escape flowers.
-
 Climate
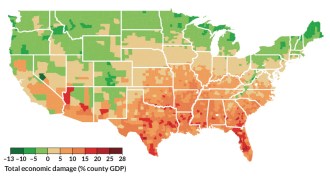
ClimateClimate change could exacerbate economic inequalities in the U.S.
Counties across the United States won’t all pay the same price for climate change, a new simulation predicts.
-
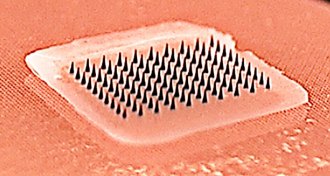 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGetting a flu ‘shot’ could soon be as easy as sticking on a Band-Aid
Microneedle patches may make home-based vaccination a reality.